The Arctic is reeling from its warmest year since at least 1900

Arctic climate change went into overdrive in 2016, with record high temperatures eclipsing anything seen since at least 1900. Accompanying the record warmth were freak losses of sea ice, melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet and a host of cascading feedbacks that scientists have been warning about for years.
The record warm year reflects both human-caused global warming, which is hitting the Arctic harder than almost any other region on Earth, as well as natural weather variability that pumped even more heat into the region this year.
Scientists detailed the changes on Tuesday with the release of an annual peer-reviewed report that amounts to a physical of the Arctic environment, known as the "Arctic Report Card."
SEE ALSO: Exxon CEO Rex Tillerson is, strangely, the most pro-climate Trump nominee
Due to human-caused global warming and natural weather patterns that acted to enhance such warming, the region scored an extremely poor grade this year.
Don Perovich, a scientist at Dartmouth University who helped prepare the report, said the Arctic is "shouting change" right now, whereas it used to "whisper change" back when the first report card was first released 11 years ago.
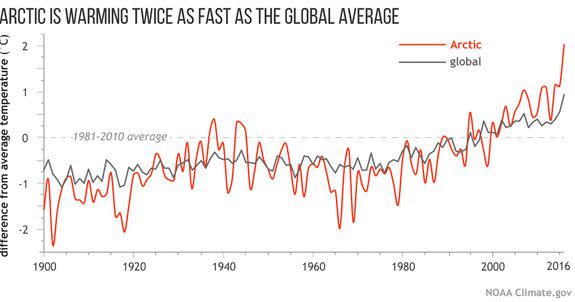
Image: noaa
At a press conference during the annual meeting of the American Geophysical Union in San Francisco, Perovich said that if he were to give a letter grade to the sea ice cover, it would be a D-plus.
His colleagues agreed. “Rarely have we seen the Arctic show a clearer, stronger or more pronounced signal of persistent warming and its cascading effects on the environment than this year,” said Jeremy Mathis, director of NOAA’s Arctic Research Program, in a press release.
Mathis said researchers are investigating how much of the Arctic warming had to do with the intense El Niño in 2015, but that untangling that mystery will take several more months.
Record air and ocean temperatures
The changes occurring throughout the Arctic, as the region warms at twice the rate of the rest of the planet, are sweeping and vivid.
Average annual air temperatures over Arctic land areas were the highest in the observational record during the year ending in September 2016, with a 3.5-degree Celsius, or 6.3 degree Fahrenheit, increase compared to 1900. Record monthly highs were set in January, February, October and November.
Such records are especially noteworthy because these months are darker months, with little if any sunshine reaching the surface of the Arctic.

Image: Ilulisat, Vestgronland, Greenland
Seeing such a temperature spike during these months reflects both warm air being transported into the region by weather patterns, as well as feedbacks between missing sea ice, open ocean waters and air temperatures.
"Those are the periods when the Arctic should be really cold,” Mathis told Mashable in an interview. “It’s one thing for the summers to be warmer, but this is [a new] trend of the winter months setting record temperatures.”
Winter air temperatures set a new record overall, with some areas seeing air temperature anomalies of 8 degrees Celsius, or 14.4 degrees Fahrenheit, above average, the report found.
Snow and Ice is vanishing
Spring snow cover extent in the North American Arctic reached the lowest level in the satellite record, which began in 1967.
Greenland began melting at the second-earliest point on record in the spring season. The amount of young, thin sea ice cover has continued to increase compared to older, thicker sea ice that is more resistant to melting.

Image: noaa
The Arctic sea ice minimum extent from mid-October 2016 to late November 2016 was the lowest since the satellite record began in 1979, and 28 percent less than the average for 1981-2010 in October, the report card found.
Arctic sea ice is thinning, with multi-year ice now comprising just 22 percent of the ice cover, compared to 78 percent for the more fragile first-year ice.
Comparatively, multi-year ice made up 45 percent of ice cover in 1985.
Perovich said sea ice loss is already large enough that it is impacting human activities, with greater access to the Arctic for ships and drilling activities. A massive, 1,000 passenger cruise ship successfully sailed through the Northwest Passage during the summer, for example.
Freak fall of 2016
This year's report card contains a supplementary report focusing on the extremes observed in the Arctic during the past few months, with record high temperatures across parts of the Arctic preventing sea ice from reforming.
From mid-October to the present, the report found, sea ice extent has been the lowest on record since satellite data began in 1979.
The report found that the cause of the record warm temperatures have been winds transporting mild air masses from mid-latitudes, with complex interactions taking place between midlatitude weather patterns and the Arctic.
Sea ice extent in November set a new record low, for example. Astonishingly high air and ocean temperatures during November caused sea ice to trail far behind typical levels, with sea ice extent ending the month at a record low.
Arctic sea ice extent averaged 3.51 million square miles for the month, which was 753,000 square miles below the 1981-2010 average for the period, according to data released Tuesday by the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) in Boulder, Colorado.
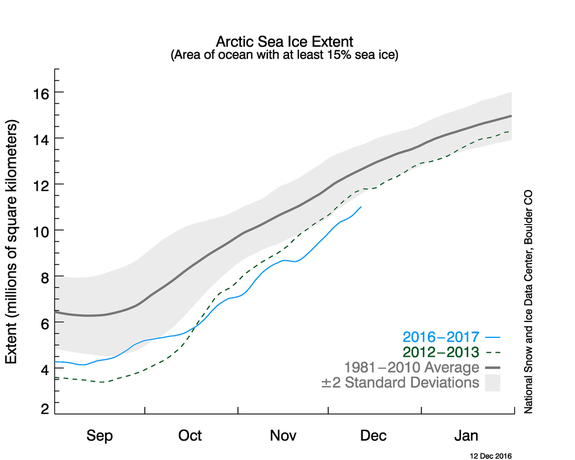
Image: NSIDC
The section of missing ice was about the same size as the entire country of Mexico. Or to put it in terms of U.S. states, the missing ice was greater than the states of Texas, California, Montana and New Mexico combined.
Research has shown that there may be connections between Arctic warming and the weather in the midlatitudes, potentially even causing more extreme weather events in the U.S. and Europe.
Ocean acidification, which is a global concern as more carbon is absorbed into ocean waters, is a greater threat to the Arctic due to the cooler water temperatures and sea ice formation there, scientists found.
When carbon dioxide dissolves in the water, a series of chemical reactions break it down in a way that reduces the amount of calcium carbonate minerals available. This process throws off the pH balance in oceans and can make it more difficult for some creatures, such as corals, snails and oysters, to function in a healthy way.
Data from the report card indicates that corrosive waters have been extending deeper into the Arctic Basin in recent years, damaging sea life, particularly shellfish. This is only likely to worsen in coming years.
Permafrost melting
In addition, on land, increasing temperatures are causing permanently frozen soils, known as permafrost, to become not-so-permanently frozen soils. This is releasing greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, making parts of the Arctic a net source of global warming pollution. It is thought that the permafrost zone that rings the Arctic from Alaska to northern Canada and around Scandinavia to Siberia contains twice as much organic carbon as is currently in the atmosphere.
If all the permafrost were to melt, it would be an utter disaster for the climate.
"Overall, tundra appears to be releasing net carbon to the atmosphere," the report states.
Outside observers say the 2016 report card is alarming and should spur action.
“The 2016 Arctic Report Card further documents the unraveling of the Arctic and the crumbling of the pillars of the global climate system that the Arctic maintains,” said Rafe Pomerance, chair of Arctic 21 and a member of the Polar Research Board of the National Academy of Sciences, in a statement.
“Governments must urgently work together to establish a future Arctic that minimizes ever greater warming from the loss of sea ice and snow cover and thawing permafrost, and massive sea level rise from the shrinking Greenland ice sheet and other Arctic glaciers.”
Scientists involved with the report card said they are hoping to get more funding to support their work by funding additional observing networks to get more real-time data from the Far North.
That may be a tough sell with the incoming Trump administration, given the administration's strong climate denial bent.

