Mars, Jupiter, Saturn and More: Don't Miss the Planet Parade Tonight's Sky
If you go out tonight (May 14) about half an hour after sunset and have clear weather, you will see a number of bright objects in the sky. The brightest of these celestial lights are four of five planets visible to the naked eye this month, with the full moon completing the view — a sight you won't want to miss.
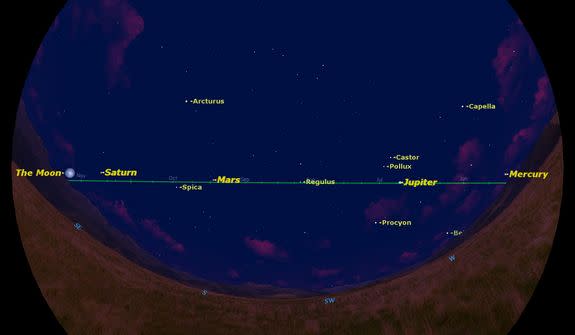
To begin our planet parade in May's night sky, let's look low in the northwest. There you can find the tiny speck of Mercury, never far from the sun. You may need a binocular to spot it.
A bit higher in the west is Jupiter, long past its opposition on Jan. 5, and now sinking rapidly behind the sun. If you have a telescope take a look to see Jupiter's four bright moons.
Due south is Mars, now well past opposition on April 8, and fading fast in brightness. If you have a powerful telescope, you might still spot the Red Planet's tiny northern polar ice cap. [Amazing Night Sky Photos for May (Gallery)]
May full moon and more
Rising in the southeast, just ahead of the full moon, is the planet Saturn, just four days past opposition.
The rising moon and Saturn mark the midpoint of the night: they will be high in the southern sky at local midnight (1 a.m. local time in most areas because of Daylight Saving Time).
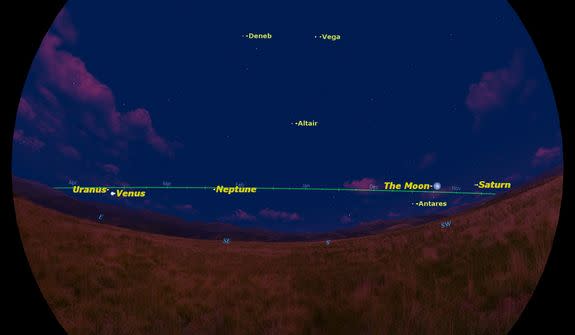
If you go out about an hour before sunrise tomorrow morning (May 15), the moon and Saturn will have moved to the southwest, where they are setting. Notice how much the moon has moved relative to Saturn during the night.
Venus will have risen low in the southeast, still very bright, although it soon will be lost in the sun's glare.
In the southeastern sky you will need binoculars to spot Neptune, the farthest planet from the sun.
Finally, Uranus, also requiring binoculars, will be close to Venus for the next few nights.
A planet parade in the night sky
Notice how all seven planets and the moon fall close to the green line which marks the ecliptic — the path the sun follows across the sky. In the sky maps in this guide, I've adjusted the view to emphasize that it is a straight line, but this is not always obvious when you see it spread across the sky. Having it marked by so many bright planets helps to visualize it.
Because all the planets and the moon follow courses close to the ecliptic, they frequently have close encounters, called conjunctions, as they pass one another. Sometimes one planet may even pass in front of another as seen from Earth, resulting in eclipses, transits, and occultations.
In April, stargazers on Earth saw two eclipses: a lunar eclipse on April 15, when the Earth cast its shadow on the moon; and an annular solar eclipse on April 29, when the moon passed in front of the sun.
This month, we will have a conjunction of Uranus and Venus on May 15 and an occultation of Saturn tonight. However, the Saturn occultation will occur while the planet and the moon were below the horizon in North America, so stargazers there will miss it. Observers in Australia, however, are well placed to see the event.
Tonight, and for the next few weeks, all seven planets are visible, making it a great opportunity for a "Solar System Marathon." How many Solar System bodies can you see in a single night?
You can also seek out an asteroid or two, a telescope view of two comets, the zodiacal light, and a meteor or two. If you are really lucky, there will be a bright display of aurora, though these have been few and far between during the current subdued solar maximum. Be sure to count the moons you see circling Jupiter and Saturn!
Editor's Note: If you take an amazing photo of the planets, or any other night sky view, that you'd like to share for a possible story or image gallery, please contact managing editor Tariq Malik at spacephotos@space.com.
This article was provided to Space.com by Simulation Curriculum, the leader in space science curriculum solutions and the makers of Starry Night and SkySafari. Follow Starry Night on Twitter @StarryNightEdu. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.
Copyright 2014 SPACE.com, a TechMediaNetwork company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.