Tiny New Moon Discovered Around Neptune
The Hubble Space Telescope has revealed a small, never-before-seen moon around Neptune, boosting the giant blue planet's total satellite count to 14 satellites, new photos reveal.
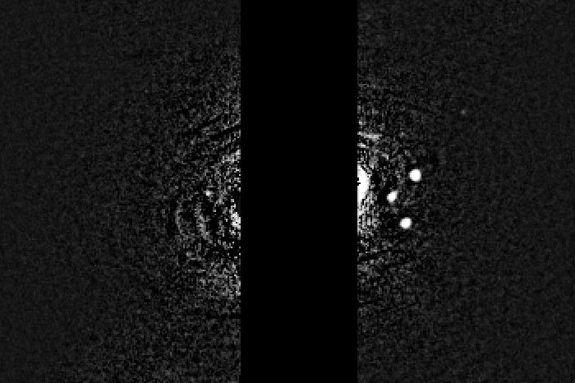
The newfound Neptune moon — called S/2004 N 1 — was discovered July 1 during a fresh analysis of older Hubble Space Telescope images, scientists said. The newly discovered satellite is Neptune's smallest known moon and is just 12 miles (19 kilometers) wide.
Hubble telescope scientists announced the new Neptune moon's discovery today (July 15). The small satellite wasn't easy to find. [See Photos of Neptune, The Mysterious Blue Planet]
"The moons and arcs [segments of rings around the planet] orbit very quickly, so we had to devise a way to follow their motion in order to bring out the details of the system," SETI Institute scientist Mark Showalter, the moon's discoverer, said in a statement. "It's the same reason a sports photographer tracks a running athlete — the athlete stays in focus, but the background blurs."
In order to find the moon, Showalter dug through archival photos taken by Hubble from 2004 to 2009. The newly found moon appears in about 150 of those photos. By plotting a circular orbit of the moon, Showalter saw that the tiny satellite fully orbits Neptune every 23 hours.
The tiny moon is so small and hard to see that it even evaded NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft when it flew by Neptune in 1989. At the time, Voyager 2 revealed six previously unknown moons in orbit around the blue planet, NASA officials have said.
S/2004 N 1 is so small that it's about 100 million times fainter than the dimmest star that can be seen with the naked eye, NASA officials said.
At 1,680 miles (2,700 km) across, Neptune's biggest moon is Triton. It is the only large moon in the solar system that has a retrograde orbit, meaning that it orbits in the opposite direction of its host planet's rotation, scientists have found.
Because of this strange orbit, some experts suspect that Triton is a dwarf planet caught in Neptune's gravitational pull.
"This capture would have gravitationally torn up any original satellite system Neptune possessed," Hubble officials wrote in a statement. "Many of the moons now seen orbiting the planet probably formed after Triton settled into its unusual retrograde orbit about Neptune."
The Hubble Space Telescope launched in 1990 and has been beaming back amazing images of celestial sights ever since. NASA officials hope to keep the venerable space telescope in operation until at least 2018 when its successor, the James Webb Space Telescope, is expected to launch.
Follow Miriam Kramer @mirikramer and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on SPACE.com.
Copyright 2013 SPACE.com, a TechMediaNetwork company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.