19 Costliest Diseases in the US

Some of the most common diseases in the United States are also some of the most expensive. They all come with the unquantifiable costs of pain and suffering, but they also have price tags with countable dollar amounts. When you put all those dollars together, the cost of what ails America reaches into the trillions. Read on to learn about the top 19 costliest diseases.
Read: 18 Medical Expenses You Can Deduct From Your Taxes
Learn: HSA vs. FSA: What's the Difference?
Last updated: Oct. 15, 2021

Influenza: $11.2 Billion
One of the few bright spots to come out of 2020 was that flu season was mild thanks to COVID precautions. But the skeptics who compared coronavirus to "just a bad case of the flu" should reconsider their analogies.
The flu is deadly serious -- and expensive.
There is more than one type of flu virus, and all types can mutate into new viral lineages, which requires costly monitoring so that adjustments can be made to the annual vaccination targets. The flu is also associated with massive indirect costs such as missed work, reduced productivity and hospital stays.
See: 10 Companies That Offer Health Insurance to Part-Time Employees

Back Problems: $12 Billion
Not only are people with chronic back pain more likely to use the healthcare system, according to the Georgetown University Health Policy Institute, but they're much more likely to miss work. Back pain causes 83 lost workdays per year. One of the biggest causes for trips to the doctor in America, back pain afflicts 16 million adults.
Find Out: The Economy and Your Money: All You Need To Know

Hyperlipidemia: $15.47 Billion
Hyperlipidemia, or excess fat in the blood -- also known as high cholesterol -- is a significant risk factor for heart disease. In all, nearly 94 million American adults suffer from the condition, which usually can be treated with prescription medication. Those medications represent the vast majority -- as much as 90% -- of the expenses associated with the disease.
Look: Should Employers Require Workers To Take Time Off?
Sexually-Transmitted Diseases (STDs): $16 Billion
Of the nearly 2.56 million reported cases of STDs in the United States, the overwhelming majority -- more than 1.8 million -- are from chlamydia. Gonorrhea comes in a distant second, followed by syphilis.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, preventative education is crucial, especially considering that more than 50% of local and state STD budgets have been slashed in recent years.

Attention Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): $8.4 Billion - $17.4 Billion
ADHD, which is associated with reduced attention and impulse control, is one of the most common and costly childhood neurodevelopmental disorders. Unlike most ailments on this list, doctors and scientists know little about both the risk factors and the causes. Behavior therapy is usually used in conjunction with medication to treat the disorder.

HIV/AIDS: $35 Billion
The vast majority of the $34.8 billion federal HIV/AIDS budget is spent on direct care for patients in the United States -- but America also contributes significantly to the global fight against AIDS. The U.S. gives $6.8 billion to worldwide HIV/AIDS treatment, education and research.

Stroke: $46 Billion
The statistics about strokes in the United States are as staggering as the cost. Someone has a stroke every 40 seconds -- that's nearly 800,000 strokes a year -- and someone dies from one every four minutes, according to the CDC.
For those who survive, a stroke often leads to permanent disability. As with so many other diseases on this list, lifestyle matters. Smoking, obesity and high blood pressure all increase the risk.
Make More: 26 Highest-Paying Jobs That Let You Work From Home

Hypertension: $48.6 Billion
Around 30% of American adults -- a full 75 million -- suffer from hypertension, known commonly as high blood pressure. Hypertension, which also can affect children, is a key driver for the No. 1 and No. 3 causes of early death in the United States -- heart disease and stroke, respectively.
High blood pressure kills roughly 400,000 people per year. The nearly $49 billion price tag associated with hypertension includes indirect costs such as medications and work absenteeism.
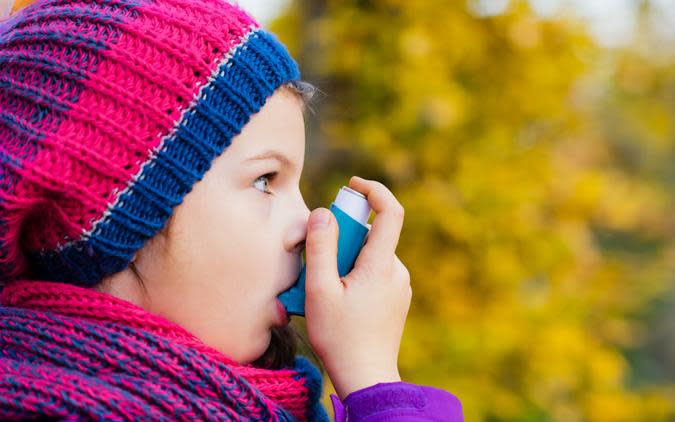

Asthma: More Than $81.9 Billion
About 25 million people in the U.S. -- roughly one in 13 Americans -- suffer from asthma, according to the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America. About 5.1 million of them are under the age of 18, making asthma the leading chronic disease in children. It's also one of the leading causes of missed school days.
But it's not just children in school. The nearly $82 billion it consumes includes indirect costs such as poor work performance and missed days. Asthma sufferers miss an average of 14 days of work per year.
Kidney Disease: More Than $118.4 Billion
A human kidney is about the size of a computer mouse -- and a pair of them are responsible for filtering every ounce of blood in the body every half hour. One in seven Americans suffers from chronic kidney disease, with the ailment going undiagnosed in most.
Even though roughly half of non-dialysis patients who suffer from the condition don't know they have it, kidney disease is the No. 9 cause of death. Among kidney patients, 75% of all new cases are the result of some combination of diabetes and high blood pressure.
It costs $81.8 billion to treat chronic kidney disease (CKD) in Medicare recipients alone, according to the CDC, with another $36.6 billion going to treat end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
Read: 10 US Cities With Plenty of Jobs and Cheap Housing

Arthritis: More Than $140 Billion
Adults with arthritis sustain $2,117 more in annual medical costs than non-sufferers, according to the CDC, and they also lose $4,040 in pay at work. Those statistics, however -- the most recent that are available -- are a few years old. The dollar figures are almost certainly higher today.
More than 30 million Americans suffer from osteoarthritis alone, and when joint replacement is necessary, it becomes one of the most expensive conditions to treat. Although the costly, painful ailment is not totally preventable, the risk for adults who exercise is much lower than the risk for those who do not.

Cancer: $200.7 Billion
The Cancer Action Network estimates that America spent more than $200 billion on cancer in 2020, up from $182.6 billion in 2015. By 2030, that number is expected to grow to $245.6 billion, a 34% increase over 2015.
According to the National Cancer Institute, 1.8 new cases of cancer were diagnosed in America in 2020 and more than 606,000 Americans died from cancer.

Mental Disorders: $225.1 Billion
Nearly one in five Americans -- more than 51 million people -- live with some form of mental illness, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. For the 18-44 demographic, depression and other mental illness is the No. 3 cause of hospitalization. On average, adults who are diagnosed with serious mental illness die 25 years earlier than those in the larger population.

Dementia: More Than $305 Billion
The cost of Alzheimer's alone -- the most common type of dementia -- is now more than $300 billion, according to research published in the American Journal of Managed Care. The cost of the chronic condition is magnified by the fact that late-stage sufferers require constant care.
Medicare pays for $155 billion, Medicaid pays for $51 billion, $66 billion is paid out of pocket and the rest is classified as "other."

Heart Disease: $318 Billion
Between 2000 and 2011, instances of heart disease declined significantly in the United States, but then the progress stalled and even reversed in the worst cases. The trend, according to a report by the American Heart Association and the American Stroke Association, is the result of massive increases in obesity, Type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure, much of which is attributed to poor diet and lack of exercise. By 2035, the organizations estimate that half of America will suffer some sort of cardiovascular disease, and costs will rise to $1.1 trillion.
More: 15 Signs Your Employer Wants You To Retire

Diabetes: $327 Billion
The American Diabetes Association conducted major studies on the illness in 2007 and then again in 2012. During that time period, the costs associated with the disease jumped from $174 billion to $245 billion -- that's a 41% increase in just five years.
Today, the cost of diabetes and pre-diabetes is well over $300 billion. Over 34 million people suffer from the ailment -- more than 10% of the population -- which dramatically increases the risk of stroke, blindness, heart disease, kidney disease and the loss of extremities.

Traumatic Injury: $671 Billion
According to the CDC, non-fatal injuries cost the country $457 billion every year, and $214 billion goes to fatal injuries. More than 3 million people have been hospitalized annually with injuries, another 27 million are treated at ERs and released. In all, 192,000 people die annually from both violence and accidental injuries. Men account for the overwhelming majority of traumatic injuries, and the statistics include injuries from falls, drug poisoning, suicides and homicide.

Neurological Disease: $789 Billion
America spends nearly $800 billion fighting the most common neurological disorders, which include Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, stroke, migraine, traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injuries. That tab, however, is cheap compared to the projected cost. The elderly population is set to double in the next decades, and by 2030, the cost of treating strokes and Alzheimer's alone is projected to top $600 billion.

Obesity: Up To $1.72 trillion
When it comes to expensive chronic illnesses, obesity is in a class by itself. According to the Milken Institute, obesity is responsible for $480.7 billion in direct health care costs, but another $1.24 trillion is lost to indirect costs -- more than 9% of the combined U.S. GDP.
The reason is that "obesity as a risk factor is by far the greatest contributor to the burden of chronic diseases in the U.S., accounting for 47.1% of the total cost of chronic diseases nationwide," according to Milken. Being seriously overweight makes it much more likely that you'll suffer from high blood pressure, diabetes, heart disease, stroke and certain types of cancer.
A little more than 3% of the population was obese in 1962. Today, it's around 40%.
More From GOBankingRates
Fourth Stimulus Checks Are Coming From These States — Is Yours on the List?
Here’s How Much You Need To Earn To Be ‘Rich’ in 23 Major Countries Around the World
Roger Wohlner contributed to the reporting for this article.
This article originally appeared on GOBankingRates.com: 19 Costliest Diseases in the US
