AI-Based Startup Optic Raises $11M to Put the ‘NF’ in NFTs
Optic, a startup that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to authenticate non-fungible tokens (NFTs), unveiled its business on Wednesday and raised $11 million in a seed round led by Kleiner Perkins and crypto-native investment giant Pantera Capital. The company will use the funds toward building out the cost-intensive infrastructure and hiring engineering talent, Optic co-founder and CEO Andrey Doronichev told CoinDesk in an interview.
Other investors in the round included Lattice Capital, OpenSea, Circle, Polygon, CoinDCX, Neon DAO and Flamingo DAO, among others.
NFTs are crypto assets with unique on-chain addresses that grant a collector or gamer ownership of that image, video, music or in-game asset, to name a few NFT use cases.
Read more: What Are NFTs and How Do They Work?
Doronichev explained that while an NFT technically is made unique by the on-chain address, its surface-level appearance to the human eye can be indistinguishable from a counterfeit.
“Without Optic, there is no real ‘NF’ in NFT,” Doronichev said.
NFT authentication
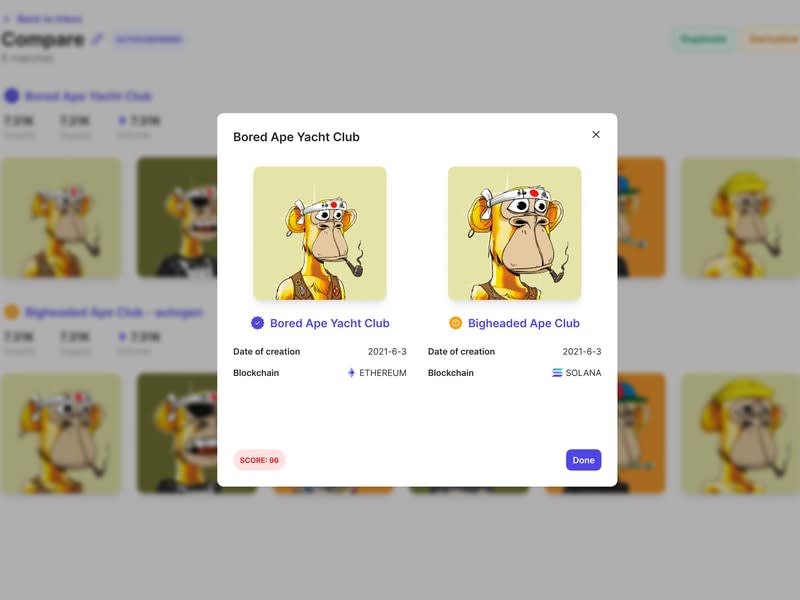
Founded in March, San Francisco-based Optic is developing an AI engine that processes the millions of new NFTs minted each day and compares the works to existing NFT collections. Optic looks for visually similarities, including flipped images, color changes or slight distortions or fuzziness. The monitoring tool informs marketplaces, brands or media companies about potential intellectual property violations.
Optic displays a percentage for how much the token matches existing NFT collections with a higher number representing the closest match and the most likely instance of an outright counterfeit. A score under 95% means the NFT probably includes inspired or derivative art, Doronichev said.
Optic’s Marketplace Moderation tool is currently used by NFT giant OpenSea as part of the company's efforts to crack down on fraud.
“Optic isn’t an enforcement business,” said Doronichev. “Our goal is to make the information available and transparent to the ecosystem. Artists and marketplaces can decide what to do with it.”
Doronichev formerly worked as a product director at Google and led the YouTube Mobile team at a time when the video platform was building its counterfeit-fighting ContentID system. He cofounded Optic with AI researchers Roman Doronin and Vlad Vinogradov, who founded Eora Data Lab, an AI studio that delivered projects for the likes of PepsiCo and Yandex.
Road Map
Optic’s near-term road map includes plans for a public application programming interface (API) for Web3 developers and new tools for NFT creators and collectors.
“People think of authenticity and all sorts of fraud and trust issues in the NFT space as a problem of a single marketplace or a single chain or a single creator or community," said Doronichev. "That's not true. That's a systemic ecosystem issue, and it has to be addressed."

