Should You Like BCE Inc.’s (TSE:BCE) High Return On Capital Employed?

Today we'll evaluate BCE Inc. (TSE:BCE) to determine whether it could have potential as an investment idea. Specifically, we're going to calculate its Return On Capital Employed (ROCE), in the hopes of getting some insight into the business.
First, we'll go over how we calculate ROCE. Then we'll compare its ROCE to similar companies. Last but not least, we'll look at what impact its current liabilities have on its ROCE.
Understanding Return On Capital Employed (ROCE)
ROCE measures the 'return' (pre-tax profit) a company generates from capital employed in its business. In general, businesses with a higher ROCE are usually better quality. Overall, it is a valuable metric that has its flaws. Author Edwin Whiting says to be careful when comparing the ROCE of different businesses, since 'No two businesses are exactly alike.
So, How Do We Calculate ROCE?
Analysts use this formula to calculate return on capital employed:
Return on Capital Employed = Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) ÷ (Total Assets - Current Liabilities)
Or for BCE:
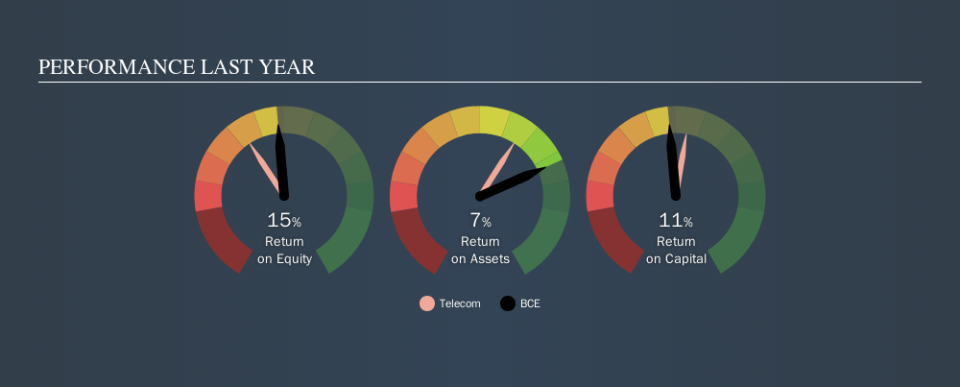
0.11 = CA$5.6b ÷ (CA$60b - CA$11b) (Based on the trailing twelve months to June 2019.)
So, BCE has an ROCE of 11%.
View our latest analysis for BCE
Does BCE Have A Good ROCE?
ROCE is commonly used for comparing the performance of similar businesses. Using our data, we find that BCE's ROCE is meaningfully better than the 6.2% average in the Telecom industry. We consider this a positive sign, because it suggests it uses capital more efficiently than similar companies. Regardless of where BCE sits next to its industry, its ROCE in absolute terms appears satisfactory, and this company could be worth a closer look.
You can see in the image below how BCE's ROCE compares to its industry. Click to see more on past growth.
When considering ROCE, bear in mind that it reflects the past and does not necessarily predict the future. Companies in cyclical industries can be difficult to understand using ROCE, as returns typically look high during boom times, and low during busts. ROCE is, after all, simply a snap shot of a single year. What happens in the future is pretty important for investors, so we have prepared a free report on analyst forecasts for BCE.
Do BCE's Current Liabilities Skew Its ROCE?
Liabilities, such as supplier bills and bank overdrafts, are referred to as current liabilities if they need to be paid within 12 months. Due to the way ROCE is calculated, a high level of current liabilities makes a company look as though it has less capital employed, and thus can (sometimes unfairly) boost the ROCE. To counteract this, we check if a company has high current liabilities, relative to its total assets.
BCE has total assets of CA$60b and current liabilities of CA$11b. As a result, its current liabilities are equal to approximately 19% of its total assets. Current liabilities are minimal, limiting the impact on ROCE.
Our Take On BCE's ROCE
This is good to see, and with a sound ROCE, BCE could be worth a closer look. BCE shapes up well under this analysis, but it is far from the only business delivering excellent numbers . You might also want to check this free collection of companies delivering excellent earnings growth.
If you are like me, then you will not want to miss this free list of growing companies that insiders are buying.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.