Did Air France-KLM SA (EPA:AF) Use Debt To Deliver Its ROE Of 22%?

Want to participate in a short research study? Help shape the future of investing tools and receive a $20 prize!
One of the best investments we can make is in our own knowledge and skill set. With that in mind, this article will work through how we can use Return On Equity (ROE) to better understand a business. We’ll use ROE to examine Air France-KLM SA (EPA:AF), by way of a worked example.
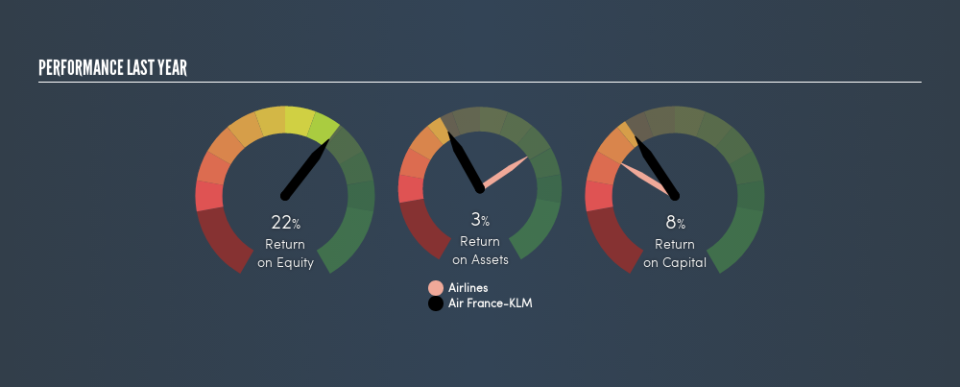
Over the last twelve months Air France-KLM has recorded a ROE of 22%. One way to conceptualize this, is that for each €1 of shareholders’ equity it has, the company made €0.22 in profit.
Check out our latest analysis for Air France-KLM
How Do You Calculate ROE?
The formula for ROE is:
Return on Equity = Net Profit ÷ Shareholders’ Equity
Or for Air France-KLM:
22% = 372 ÷ €1.9b (Based on the trailing twelve months to December 2018.)
Most know that net profit is the total earnings after all expenses, but the concept of shareholders’ equity is a little more complicated. It is all earnings retained by the company, plus any capital paid in by shareholders. Shareholders’ equity can be calculated by subtracting the total liabilities of the company from the total assets of the company.
What Does ROE Signify?
ROE measures a company’s profitability against the profit it retains, and any outside investments. The ‘return’ is the yearly profit. The higher the ROE, the more profit the company is making. So, all else equal, investors should like a high ROE. That means ROE can be used to compare two businesses.
Does Air France-KLM Have A Good Return On Equity?
By comparing a company’s ROE with its industry average, we can get a quick measure of how good it is. Importantly, this is far from a perfect measure, because companies differ significantly within the same industry classification. If you look at the image below, you can see Air France-KLM has a similar ROE to the average in the Airlines industry classification (22%).
That’s neither particularly good, nor bad. ROE can give us a view about company quality, but many investors also look to other factors, such as whether there are insiders buying shares. If you like to buy stocks alongside management, then you might just love this free list of companies. (Hint: insiders have been buying them).
The Importance Of Debt To Return On Equity
Most companies need money — from somewhere — to grow their profits. That cash can come from issuing shares, retained earnings, or debt. In the first and second cases, the ROE will reflect this use of cash for investment in the business. In the latter case, the debt required for growth will boost returns, but will not impact the shareholders’ equity. In this manner the use of debt will boost ROE, even though the core economics of the business stay the same.
Combining Air France-KLM’s Debt And Its 22% Return On Equity
We think Air France-KLM uses a lot of debt to boost returns, as it has a relatively high debt to equity ratio of 5.97. So although the company has an impressive ROE, that figure would be a lot lower without the use of debt.
But It’s Just One Metric
Return on equity is a useful indicator of the ability of a business to generate profits and return them to shareholders. In my book the highest quality companies have high return on equity, despite low debt. If two companies have the same ROE, then I would generally prefer the one with less debt.
But ROE is just one piece of a bigger puzzle, since high quality businesses often trade on high multiples of earnings. Profit growth rates, versus the expectations reflected in the price of the stock, are a particularly important to consider. So you might want to check this FREE visualization of analyst forecasts for the company.
Of course, you might find a fantastic investment by looking elsewhere. So take a peek at this free list of interesting companies.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.