Can Enghouse Systems Limited (TSE:ENGH) Improve Its Returns?

One of the best investments we can make is in our own knowledge and skill set. With that in mind, this article will work through how we can use Return On Equity (ROE) to better understand a business. By way of learning-by-doing, we'll look at ROE to gain a better understanding of Enghouse Systems Limited (TSE:ENGH).
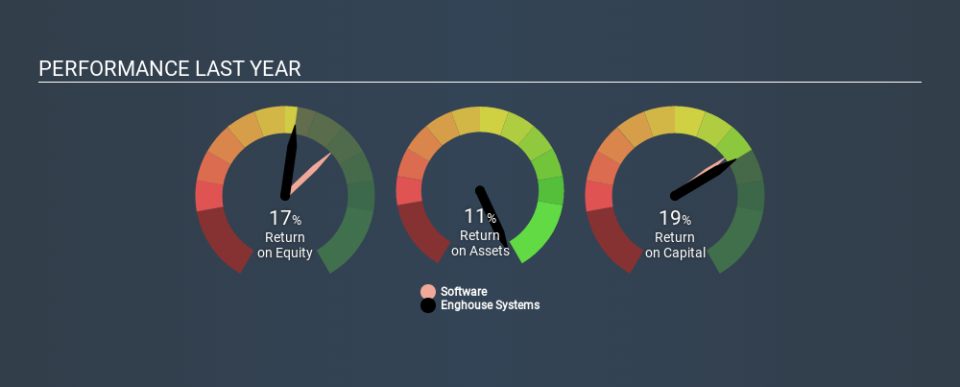
Enghouse Systems has a ROE of 17%, based on the last twelve months. That means that for every CA$1 worth of shareholders' equity, it generated CA$0.17 in profit.
View our latest analysis for Enghouse Systems
How Do I Calculate ROE?
The formula for return on equity is:
Return on Equity = Net Profit ÷ Shareholders' Equity
Or for Enghouse Systems:
17% = CA$66m ÷ CA$380m (Based on the trailing twelve months to July 2019.)
It's easy to understand the 'net profit' part of that equation, but 'shareholders' equity' requires further explanation. It is all earnings retained by the company, plus any capital paid in by shareholders. The easiest way to calculate shareholders' equity is to subtract the company's total liabilities from the total assets.
What Does ROE Mean?
Return on Equity measures a company's profitability against the profit it has kept for the business (plus any capital injections). The 'return' is the yearly profit. The higher the ROE, the more profit the company is making. So, as a general rule, a high ROE is a good thing. That means it can be interesting to compare the ROE of different companies.
Does Enghouse Systems Have A Good Return On Equity?
By comparing a company's ROE with its industry average, we can get a quick measure of how good it is. However, this method is only useful as a rough check, because companies do differ quite a bit within the same industry classification. If you look at the image below, you can see Enghouse Systems has a lower ROE than the average (23%) in the Software industry classification.
That certainly isn't ideal. We'd prefer see an ROE above the industry average, but it might not matter if the company is undervalued. Nonetheless, it could be useful to double-check if insiders have sold shares recently.
How Does Debt Impact ROE?
Most companies need money -- from somewhere -- to grow their profits. That cash can come from issuing shares, retained earnings, or debt. In the first and second cases, the ROE will reflect this use of cash for investment in the business. In the latter case, the use of debt will improve the returns, but will not change the equity. That will make the ROE look better than if no debt was used.
Combining Enghouse Systems's Debt And Its 17% Return On Equity
Although Enghouse Systems does use a little debt, its debt to equity ratio of just 0.0019 is very low. Its very respectable ROE, combined with only modest debt, suggests the business is in good shape. Conservative use of debt to boost returns is usually a good move for shareholders, though it does leave the company more exposed to interest rate rises.
The Key Takeaway
Return on equity is a useful indicator of the ability of a business to generate profits and return them to shareholders. A company that can achieve a high return on equity without debt could be considered a high quality business. If two companies have the same ROE, then I would generally prefer the one with less debt.
But when a business is high quality, the market often bids it up to a price that reflects this. The rate at which profits are likely to grow, relative to the expectations of profit growth reflected in the current price, must be considered, too. So you might want to take a peek at this data-rich interactive graph of forecasts for the company.
But note: Enghouse Systems may not be the best stock to buy. So take a peek at this free list of interesting companies with high ROE and low debt.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Thank you for reading.