Forensic breakthrough as scientist reveals face of only person discovered crucified in Britain
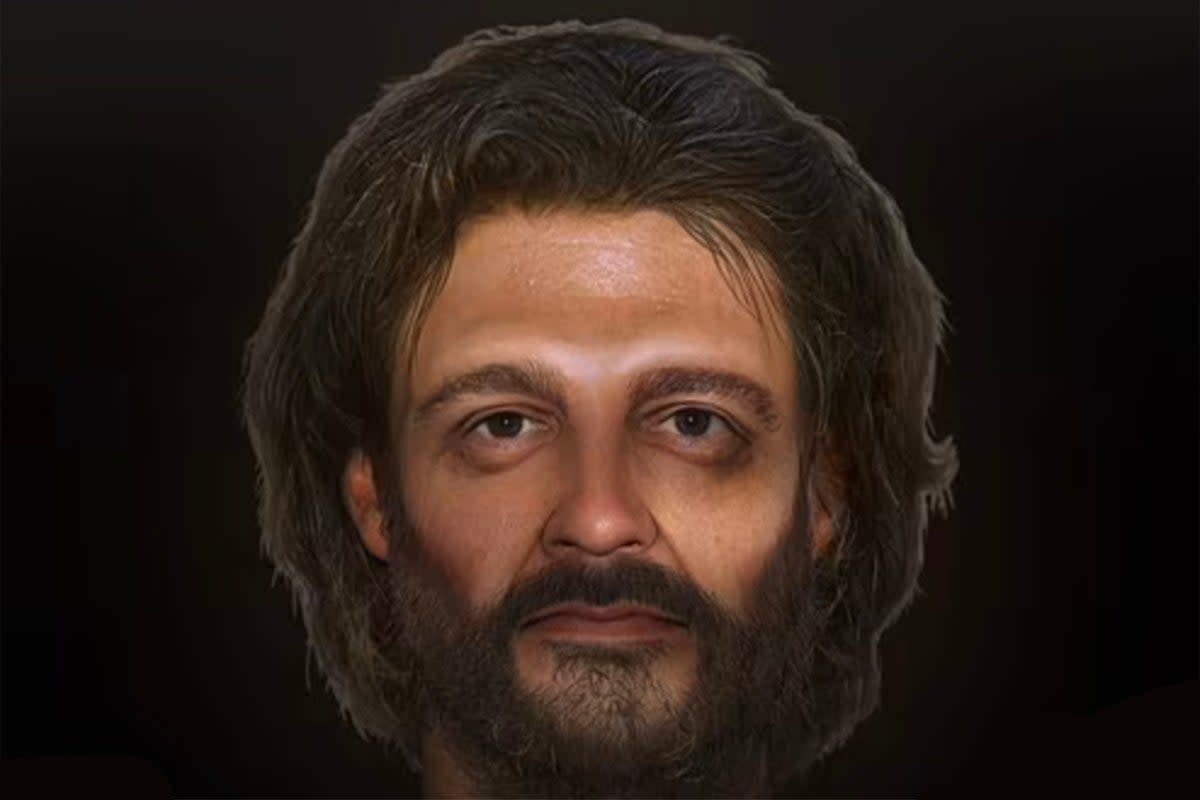

A forensic artist has recreated the face of the only man discovered crucified in Roman Britain, some 2,000 years ago - declaring “I am staring at a face from thousands of years ago”.
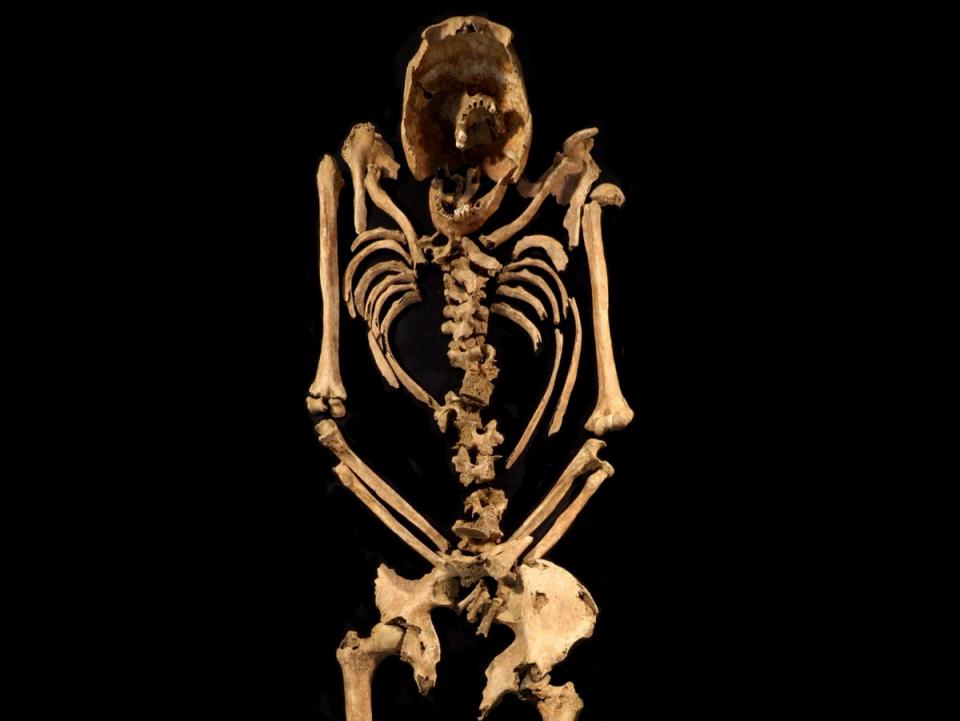
The reasons for the man being killed in such an agonising way remains a mystery, but his remains, found in Cambridgeshire three years ago, show a two inch nail had been driven through his heel bone.
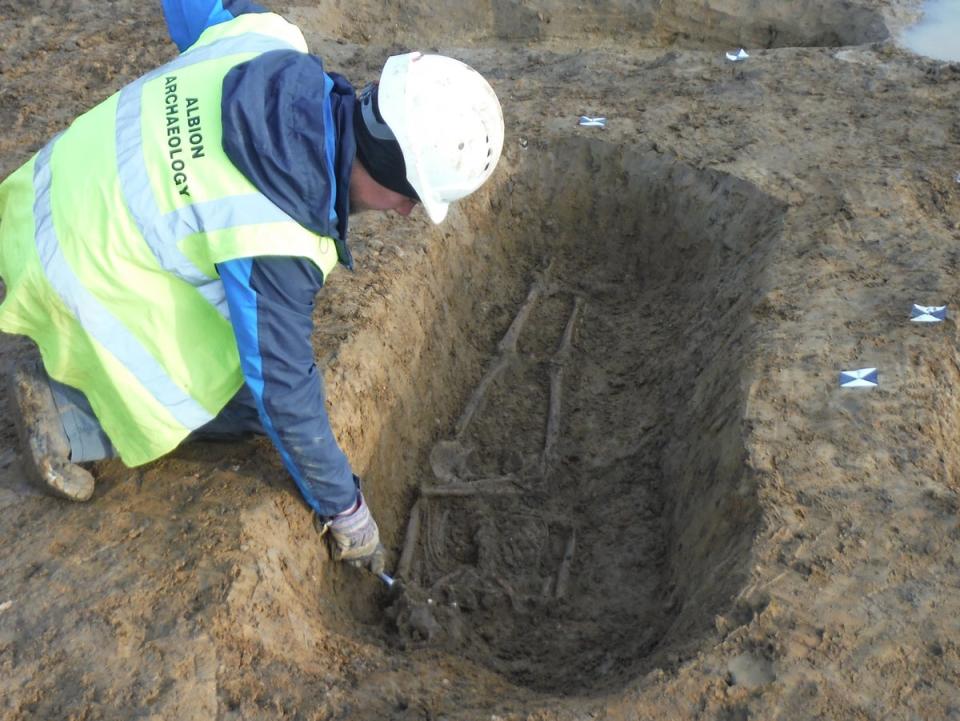
An excavation in Fenstanton in 2017 led to the discovery of his grave, and the skeleton was found in 2021. The man is estimated to have been 5’7’’ tall and in his mid-30s when he died.
Radiocarbon dating placed his death to between the years 130AD and 337AD - at a time his grave would have been at a Roman settlement between Roman Cambridge and Godmanchester.
The man, among dozens of bodies found at the site of a new housing development, was only the second Roman crucifixion victim ever found in the world. The first was unearthed in Israel in 1968.
A new BBC 4 documentary The Cambridgeshire Crucifixion shows how his face was reconstructed using DNA and forensic information obtained from his remains.
Professor Joe Mullins, of George Mason University in Virginia, US, who works with the police to rebuild the faces of crime victims, carried out the reconstruction.
Using DNA and isotopic information, Prof Mullins and colleagues concluded he was likely to have had brown hair and brown eyes. Thinning of his legs, punitive injuries and signs of immobilisation all pointed to his having been crucified.
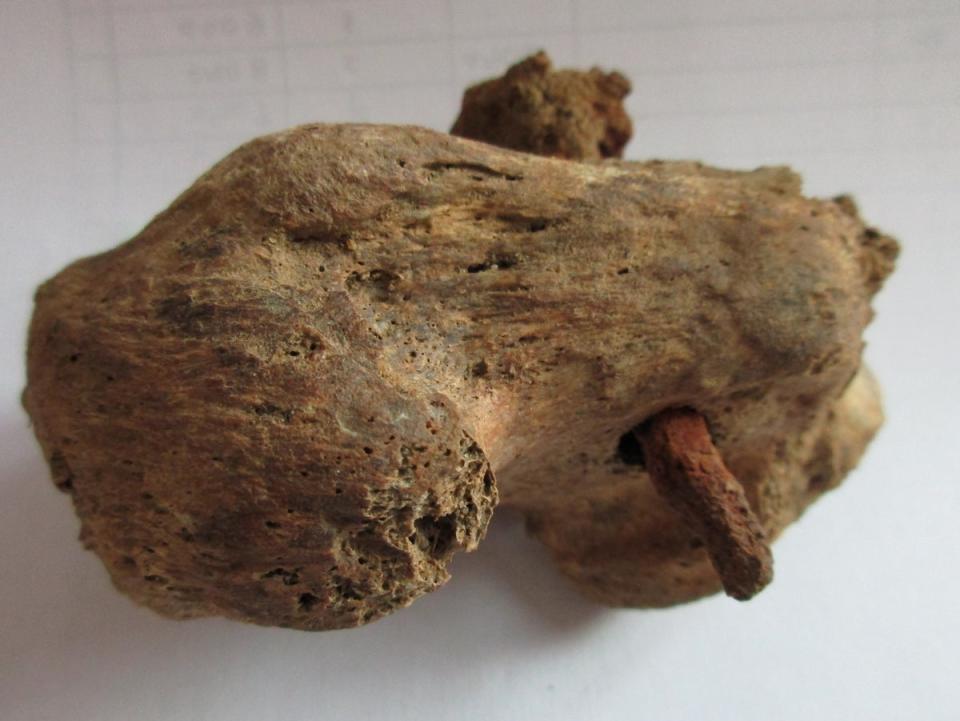

In tradition, crucifixions were carried out by nailing limbs to wood in a cross, but Romans sometimes instead tied the limbs in place with rope.
This was part of a cruel, ancient method of slow punishment of both miscreants of crimes and a vast number of slaves who were crucified because of minor misdemeanours.
This form of punishment was eventually abolished by Constantine I in the 4th-century AD.
The Cambridgeshire man is thought to have been killed half a mile from the cemetery in which he was buried.
Professor Mullins says in the programme the case was fascinating because he had just as much or more information than for a modern-day case.
He said: “Now the problem was this skull – it was fragmented. There is no other way to explain it. It was putting together a puzzle.

“It’s not just a skull any more – I am staring at a face from thousands of years ago, and staring at this face is something I will never forget.”
When the skeleton was found, human bone specialist Corinne Duhig, of Cambridge University’s Wolfson College, described it as “almost unique” due to its “good preservation” and the nail remaining in the bone.
She said: “This shows that the inhabitants of even this small settlement at the edge of empire could not avoid Rome’s most barbaric punishment.”

