Hubble Space Telescope captures 'spokes' moving across Saturn's rings
- Oops!Something went wrong.Please try again later.
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has captured "spokes" moving across Saturn's rings, a phenomenon that indicates the start of the planet's autumnal equinox in its northern hemisphere, CNN reports. The equinox will occur on May 6, 2025.
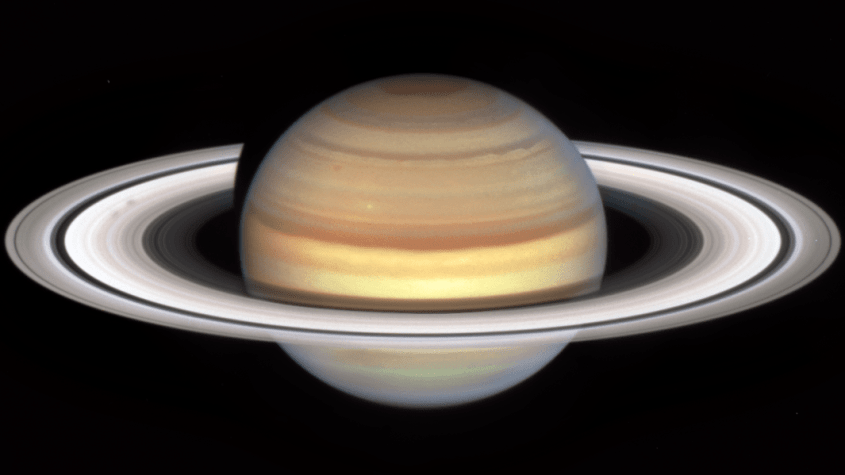
NASA, ESA, and Amy Simon (NASA-GSFC); Image Processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI)
The reason for the spokes has yet to be discovered, however the "suspected culprit for the spokes is the planet's variable magnetic field," according to NASA. "Planetary magnetic fields interact with the solar wind, creating an electrically charged environment." The space agency compares the phenomenon to the northern lights on Earth.
NASA is hoping that Hubble's new data will either confirm or deny this theory based on the previous data from Voyager and Cassini, which was a designated Saturn probe. "Despite years of excellent observations by the Cassini mission, the precise beginning and duration of the spoke season is still unpredictable, rather like predicting the first storm during hurricane season," explained Amy Simon, a senior planetary scientist at NASA.
The spokes were last seen in the 2000s. Like Earth, Saturn also experiences seasons, however since Saturn's orbit is much longer than Earth's, each season lasts around seven years. The spokes appear as the planet gets close to its equinox where the rings are tilted toward the sun. The spokes disappear near Saturn's summer or winter solstice.
NASA also explains that while the phenomenon could also occur on other ringed planets like Uranus and Neptune, it has only been observed on Saturn so far. "It's a fascinating magic trick of nature we only see on Saturn — for now at least," remarked Simon.
You may also like
5 entertaining cartoons about Biden's State of the Union address
United Airlines flight plunged to within 800 feet of Pacific Ocean

