This Louisiana archeological site still baffles scientists

LOUISIANA (KLFY) — In Louisiana sits one the United States oldest indigenous cultural and historical sites, but years on from its discovery scientists still debate what it was used for.
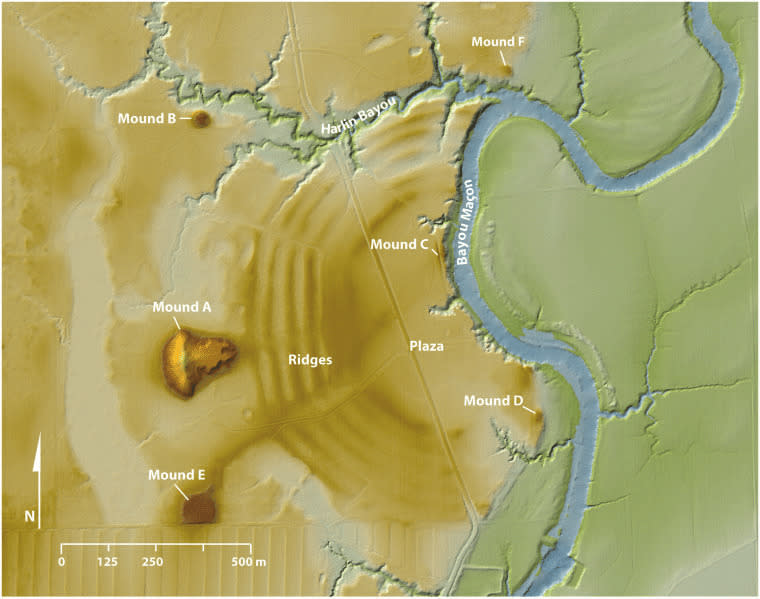
Located in West Carroll Parish in northeastern Louisiana, sits a prehistoric earthwork known as Poverty Point. The earthworks of Poverty Point consist of six C-shaped ridges that extend to the edge of the Macon Ridge and several mounds outside and inside the C-shaped ridges. This style of earthwork has yet to be found anywhere else and is unique to Poverty Point.

These fictional characters are from Louisiana
Archeologist have determined through radio carbon dating that construction of the site began as far back as 1700 BCE and continued to about 1100 BCE. For perspective, around this same time the last woolly mammoth died and the species became extinct, the Bronze Age started in China and Egypt began using yeast in bread. The site was built by the Poverty Point culture, a group of prehistoric indigenous people who inhabited the lower Mississippi Valley and Gulf coast.
The people of Poverty Point were hunter-fisher-gathers rather than agriculturalist. They are one of the few examples of complex hunter-gatherer societies that constructed large-scale monuments. The vast majority of prehistoric sites, like Stonehenge and the Pyramids of Egypt, were constructed by agricultural societies. Because of this, archeologist struggle to determine what the function of Poverty Point could have been used for.
Thanks for signing up!
Watch for us in your inbox.
Subscribe Now
KLFY Daily Digest
One of the main questions regarding the site is whether or not Poverty Point was used for a settlement or only for periodic events. Postholes have been found, along with hearths and ovens on the tops of the ridges, indicating there may have been buildings at one time. Others believe that regular residence there would have produced more postholes than what currently exist. Discussion on the sites use as a trading center has been considered, as well as having religious purposes due to some believing the ridges and aisles of the site have astronomical significance.
Poverty Point is featured in the Netflix series, Ancient Apocalypse (2022), which follows British writer Graham Hancock as he travels to different archeological sites around the global in search of lost civilizations. In episode six of the series, he travels to the United States with one of his stops being Poverty Point. Graham points out that the site could have astronomical significance, and be evidence of knowledge handed down from a lost, more advanced ancient civilization.
Aside from any conspiracies and disagreements among archeologist, there is one thing that they can all agree upon, which is the site’s historical significant and the quest to continue researching it. Since Poverty Point’s discovery in the 1830’s, much of the site as been excavated and preserved. In 2014 the site gained international recognition by becoming a UNESCO World Heritage Site, cementing its historical importance and joining a list of some of the world’s most prestigious archeological sites. This designation made Poverty Point Louisiana’s first and only World Heritage Site and the 22nd in the United States.
Today, Poverty Point National Monument is open for visitors daily from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m, with exception for certain holidays. For more information of Poverty Point and how to visit, you can access the official website here.
Latest Posts
Donald Trump Jr. receives letter containing white powder at his home
Phones are distracting students. More states want schools to ban them
Photographer accuses Taylor Swift’s dad of punching him in the face
For the latest news, weather, sports, and streaming video, head to KLFY.com.
