Micron Seeks Other Avenues for Growth Amidst China's Ban
A big blow has come to Micron Technology Inc. (NASDAQ:MU) due to an unfavorable cybersecurity review outcome from China. The considerable revenue loss from being banned in China may affect the fundamentals of the company much deeper. However, a few robust bullish catalysts for Micron remain, such as proactive performance measures and a rapid shift towards Japan.

MU Data by NASDAQ:NVDA) for the RTX 4070TI, position the company well for growth in the graphics segment.
In the mobile and intelligent edge markets, Micron expects slight declines in smartphone units for 2023 but foresees improved mobile customer inventories and a bit of shipment growth in the second half of the fiscal year. The upcoming revenue from the 1-beta 16GB LP5X and successful mobile customer design wins further highlight the company's commitment to this segment.
Micron's revenue growth in the automotive sector is expected to continue, driven by the qualification and shipment of advanced automotive storage solutions. Stability in customer inventories in the industrial segment also indicates a potential improvement in demand in the latter half of fiscal 2023.
The setback with China's ban
The ban imposed by China on Micron's products due to alleged cybersecurity risks has raised concerns about the company's prospects. Notably, sales to China accounted for about 11% of the company's revenue in past earnings results. With the ban in place, Micron will likely endure a decline in revenue in the short term. While the ban is narrowly focused on critical information infrastructure (CII) operators, the overall impact on revenue may reach that level. However, a more realistic estimate from Bloomberg suggests a low-single-digit percentage impact in the near term.

Source: Bloomberg
However, it's worth it to note that Micron's fiscal second quarter 2023 revenue shows a decline of 10% quarter-over-quarter and a significant 53% year-over-year decrease. The revenue reduction could intensify due to the ban in China. The loss of a substantial market like China and the ban's impact on sales can further contribute to a decline in Micron's financial performance in the short term.
China plays a vital role in the electronics supply chain, and the ban could disrupt Micron's supply chain and customer relationships globally. The ban may lead to challenges in meeting demand for Micron's products, resulting in potential complications and hurdles soon. Managing supply chain disruptions and maintaining customer relationships will be critical for Micron's success.
Micron operates in a highly competitive industry, facing intense competition. The ban on Micron's products in China may allow its competitors to strengthen their market positions in the country. Aggressive pricing strategies by competitors could also impact Micron's market share and profitability. Consolidating competitors may disadvantage Micron, as larger corporations with greater resources and manufacturing scale could gain a stronger position in the market.
Further, the ban on Micron may intensify China's abiliity to enhance its domestic chip-making capabilities and reduce its reliance on foreign technology. While China's chip-making ability is currently limited compared to the U.S. and Europe, the ban could accelerate China's efforts to acquire or develop cutting-edge chip technologies. As a result, it poses a potential threat to Micron in global markets as China aims to achieve self-sufficiency in advanced chip technologies.
Progressive performance measures
Micron is concentrating on progressive performance by maintaining its technological competitiveness while managing node ramps to align bit supply with demand. In terms of DRAM, the company has made significant progress in transitioning from 1-alpha to 1-beta, with 1-alpha representing the majority of its DRAM bit production. As a result, the yields on 1-alpha DRAM and 176-layer NAND have reached record levels, surpassing any previous node in the company's history. Additionally, the targeted yields for 1-beta DRAM and 232-layer NAND have been achieved ahead of schedule, showcasing the company's efficiency.
Micron has also made strides in NAND production, with 176- and 232-layer nodes now accounting for over 90% of NAND bit production. In particular, QLC (quad-level cell) NAND accounted for more than 20% of the company's NAND bit production and shipments in the fiscal second quarter. These developments indicate Micron's commitment to enhancing its technology and optimizing its production processes.
Looking forward, Micron aims to introduce its EUV (Extreme Ultraviolet)-based 1-gamma node in 2025, expected to deliver competitive performance, power efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and increased density. This forward-looking approach indicates Micron's commitment to technological advancement and its drive to maintain a competitive edge in the memory and storage markets.
Notably, Micron is reducing its supply by adding additional reductions to its fiscal 2023 capex plan. It now expects to invest approximately $7 billion, which represents a decrease of more than 40% YoY, with WFE (Wafer Fab Equipment) down by over 50% YoY. Furthermore, Micron has reduced DRAM and NAND wafer production by approximately 25%, further aligning its supply with market demand.
Micron is also focusing on reducing operational expenses. The company anticipates an overall headcount reduction of around 15%, achieved through a combination of workforce reductions and anticipated attrition throughout the calendar year. These cost-cutting measures reflect Micron's commitment to improving its operational efficiency.
While Micron has faced competitive pressures in the market, the company has maintained its flat bit-share strategy. In addition, it has reduced prices to remain competitive but has not pursued price reductions to gain market share, recognizing that customer share changes are often temporary. This strategy demonstrates Micron's focus on long-term stability and sustainable growth.
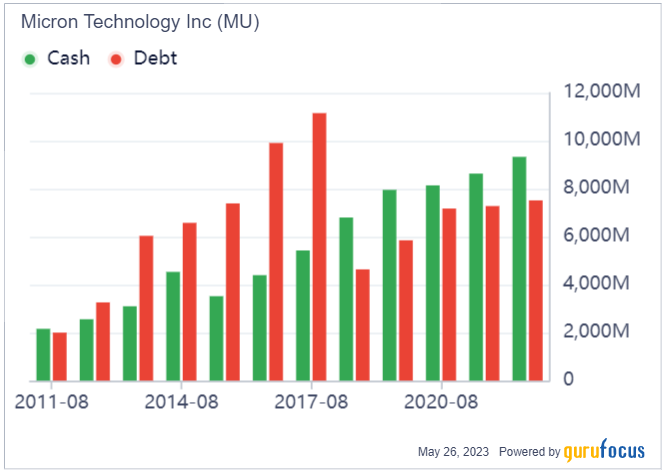
In terms of financial resilience, Micron boasts a strong balance sheet among pure-play memory and storage companies. Moreover, its robust liquidity position ensures the company can weather market downturns while maintaining its competitiveness in its product and technology.
Shifting towards Japan
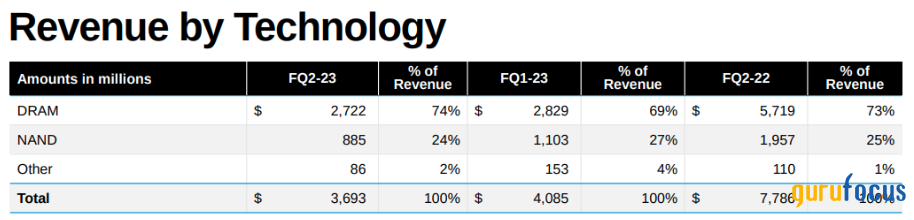
Micron's investment of $3.6 billion in Japan for DRAM chip production represents a significant step toward bolstering chip manufacturing capabilities and strengthening the chip supply chain. In addition, DRAM technology represents 74% of its revenue as of the second quarter of fiscal 2023. Therefore, the move will have significant implications for Micron's value growth.
Source: Investor Presentation
Additionally, Micron is set to receive approximately $1.5 billion in financial incentives from the Japanese government. This significant investment aims to support Micron's production of next-generation memory chips in Japan, which will contribute to the country's efforts to strengthen its domestic semiconductor industry and reduce dependence on chip imports. The move comes at a time of escalating tensions between the U.S. and China, making it crucial for Japan to enhance its chip manufacturing capabilities.
The financial support from the Japanese government will be utilized by Micron to install advanced chip-making equipment using EUV lithography technology at its facility in Hiroshima. This cutting-edge EUV technology will enable Micron to produce the next generation of DRAM chips, known as 1-gamma chips (with advanced end-to-end technology). These 1-gamma chips are expected to have the world's smallest cell size, offering faster, more power-efficient and higher-performance memory products.
Interestingly, the Japanese government has already allocated substantial funding for various chip-related projects, such as the development of 2-nanometer chips by Rapidus and the establishment of a joint chip research center. These initiatives demonstrate Japan's commitment to nurturing a robust domestic semiconductor industry and attracting major chipmakers to set up fabrication facilities in the country.
The Hiroshima facility holds strategic importance for Micron, as it houses the company's top engineers and has been the focus of previous investments. Micron's decision to use EUV lithography in Japan highlights the significance of this location and its role in the global supply chain. Furthermore, Micron's commitment to increasing chip production in the United States, as evidenced by its investment in a semiconductor factory in New York, aligns with its efforts to secure domestic manufacturing capabilities that, in turn, sustain long-term earnings momentum.
Takeaway
In conclusion, Micron Technology's strategic shift towards Japan for DRAM chip production, coupled with the financial incentives provided by the Japanese government, represents a significant step in bolstering its chip manufacturing capabilities and mitigating potential losses from China's ban.
While the prohibition poses revenue concerns and disrupts the supply chain, Micron remains resilient through proactive performance measures. Moreover, Micron's commitment to increasing chip production in the United States further secures its long-term earnings momentum. Despite challenges and intensified competition, I believe Micron is well-positioned for future growth.
This article first appeared on GuruFocus.