Milky Way Glitters in Most Enormous Image Ever
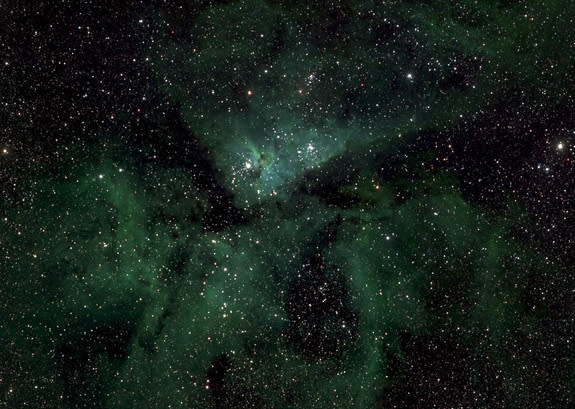
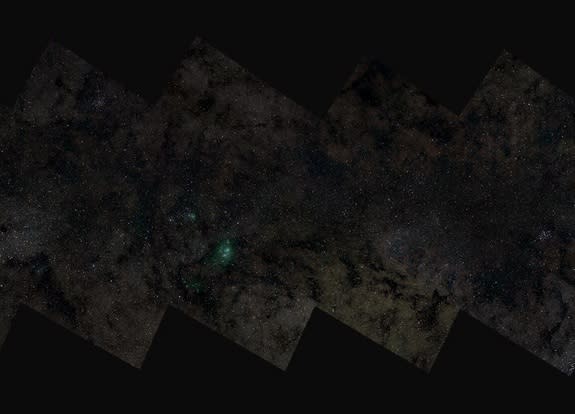
A new, insanely massive picture of the Milky Way — 46 billion pixels across — marks the largest astronomical image of all time, researchers say. It's so big, it we can only show part of it on this page.
The amazing view of the Milky Way was built out of 268 individual views of the galaxy that includes the sun and the Earth, captured night after night over the course of five years with telescopes in Chile's Atacama Desert. Astronomers at Ruhr-Universität Bochum used the data to examine stars whose brightness changes over time — and the image portrays more than 50,000 new objects with variable brightness that have never been recorded before.
The researchers made the zoom-able, searchable image available their website, so galactic explorers can scroll across the Milky Way and examine its famous and lesser-known features with more detail than ever before.
The researchers photographed every one of the 268 areas of the sky "in intervals of several days" over the course of the 5 years, the researchers said in a statement. And once they had them all, they were incorporated during a several-week calculation period.
The lead author of the new work, Moritz Hackstein, needed this incredible level of detail to pinpoint how stars were changing in the sky: Stars with planets orbiting them or systems with multiple stars will vary from brighter to dimmer during different parts of the orbit, for instance, and some stars intrinsically pulse brighter and dimmer or ignite into supernovas.
To identify any changes to the Milky Way's stars, multiple photos have to be taken over time and compared. The researchers found 64,151 variable sources of light in total — and 56,794 of them had never been seen before.
Email Sarah Lewin at slewin@space.com or follow her @SarahExplains. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.
Copyright 2015 SPACE.com, a Purch company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.