'Once-in-a-lifetime event:' Best places to see rare nova explosion from Florida
You may get to see a new — and temporary — star in the sky this year.
A massive explosion 3,000 lightyears away known as a nova event that happens more or less every 80 years will be bright enough to be visible with the naked eye, NASA said.
“It’s a once-in-a-lifetime event that will create a lot of new astronomers out there, giving young people a cosmic event they can observe for themselves, ask their own questions, and collect their own data,” said Dr. Rebekah Hounsell, an assistant research scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland who specializes in nova events. “It’ll fuel the next generation of scientists.”
Here's what will happen and how to watch.
What is the Nova Event?
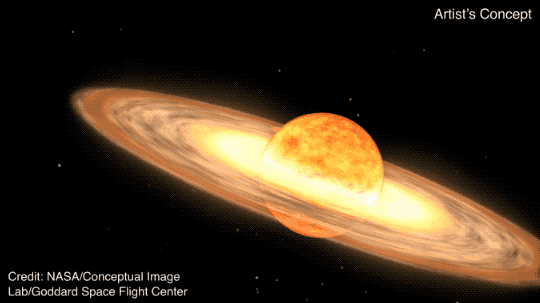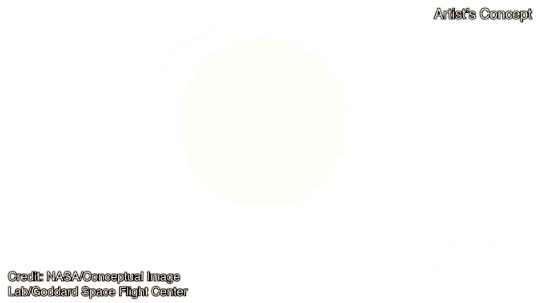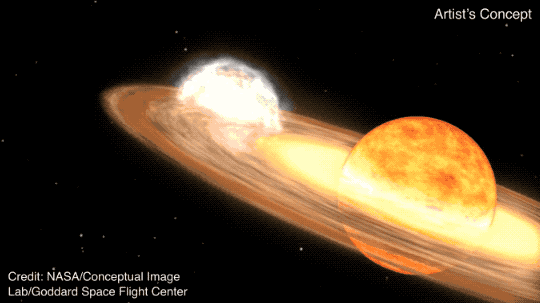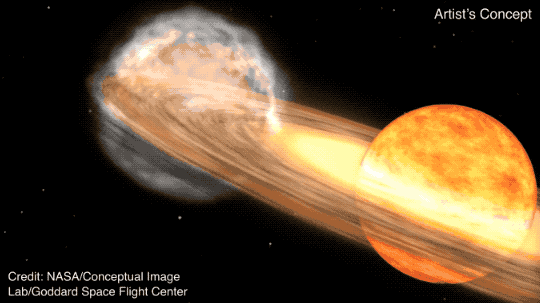
The star system T Coronae Borealis — nicknamed the "Blaze Star" and called T CrB by astronomers — is a binary system, which means it has two stars instead of just one like ours. The red giant star and white dwarf star in T CrB are orbiting each other.
The two stars are close enough that the old red giant star is slowly being stripped of its hydrogen by the gravity of the denser white dwarf, an Earth-sized chunk of dead star, NASA said. When enough material has built up on the white dwarf to raise its temperature and mass to a tipping point, it erupts in what's being called the Nova Event, also called a recurrent or repeating nova.
"The hydrogen from the red giant accretes on the surface of the white dwarf, causing a buildup of pressure and heat," NASA said. "Eventually, it triggers a thermonuclear explosion big enough to blast away that accreted material."
What's the difference between a nova explosion and a supernova?
Supernovas are a one-time deal. Stars go supernova, "a final, titanic explosion" according to NASA, at the end of their life when their mass is about eight times that of our sun and their cores collapse.
Repeating or recurrent novas are caused by other reasons and can erupt more frequently. The one from T CrB is a surface explosion when the built-up matter is flung into space, leaving the star intact. There are 10 known recurrent novas in the Milky Way galaxy, according to physicist Jordi José and astrophysicist Margarita Hernanz.
When is the Nova Event happening?
Good question. Astronomers have no way of knowing precisely and it could be years.
But astronomers say the stars are behaving similarly to the way they did in the time leading up to the last explosion seen in 1946, so it should happen sometime between now and September.
“Recurrent novae are unpredictable and contrarian,” said Dr. Koji Mukai, a fellow astrophysics researcher at NASA Goddard. “When you think there can’t possibly be a reason they follow a certain set pattern, they do – and as soon as you start to rely on them repeating the same pattern, they deviate from it completely. We’ll see how T CrB behaves.”
When it does happen, it will be quick. NASA said that at peak brightness, the nova should be visible to the naked eye for several days and just over a week with binoculars before it dims again.
How can I find the Nova Event at T Coronae Borealis?

T Coronae Borealis is in the Corona Borealis or “Northern Crown” constellation, a horseshoe-shaped curve of stars west of the Hercules constellation.
To find it after sunset, locate the two brightest stars in the Northern Hemisphere, Arcturus and Vega, and track a straight line between them to find the Northern Crown. When it happens, the nova will be visible in that region.
If you have night sky tracking apps on your phone, search for Corona Borealis.
Where are the best places to watch the Nova Event in Florida?
Kissimmee Prairie Preserve State Park Named Florida. source https://t.co/Dsff6eIJXE https://t.co/zzyCXAAmUf pic.twitter.com/oxWJ1ETCLo
— Space (@redditSpaceView) April 18, 2018
With a clear sky — we know, we know — you should be able to see the initial explosion from your front yard. But the farther away from light pollution you can get, the better. If you can, go to a rural or empty area with as little light as possible or head to the beach away from hotels and condos and find a spot with a clear, unclouded view of the night sky.
If you really want a good look, consider heading to a state park, local campground or astronomy location for nice, inky-black skies. Here are some popular one for stargazers:
Kissimmee Prairie Preserve State Park: Recognized as Florida's first Dark Sky Park and possibly the darkest spot in Florida.
Big Cypress National Preserve in South Florida: The second official Dark Sky Park with 729,000 acres of rugged, untouched Florida wilderness.
Dr. Julian G. Bruce St. George Island State Park: Far from major city lights, the park even has an observation platform built by volunteers just for watching the skies.
Chiefland Astronomy Village, about an hour west of Gainesville: Run by non-professional stargazers but open to the public with showers, a clubhouse, restrooms, a picnic area, electricity, and 360 degrees of horizon with nothing in the way.
Sebastian Inlet State Park: An amazing panoramic view of the sky over the Atlantic.
Fakahatchee Strand Preserve: Hard to get much darker than the Everglades at night.
Cedar Key Scrub State Reserve: Over 5,000 acres in the Florida Keys with a nearly unbroken horizon for a panoramic view.
Waccasassa Bay Preserve State Park: Waccasassa Bay, in the town of Inglis, is only accessible by boat but it sets the stage for a spectacular view with the horizon broken only by tree islands of red cedar, cabbage palm and live oak.
Fox Observatory in Markham Park in the city of Sunrise: An observatory open to the public every Saturday night, rain or shine.
Bahia Honda State Park on Big Pine Key in the Florida Keys: One of the best places to see stars in Florida and one of the only places in the U.S. where you can see the Southern Cross constellation
Julia Gomez, USA TODAY and Iris Seaton, Asheville Citizen Times/USA TODAY Network contributed to this story.
This article originally appeared on The Daytona Beach News-Journal: Nova explosion to appear as 'new star.' How to watch in Florida

