‘I pay £0 for my energy bills – thanks to my heat pump and 20 solar panels’

The nights are getting longer and the days colder. Energy use is at its peak – whether you rely on heating oil, a gas boiler or a heat pump to stay warm.
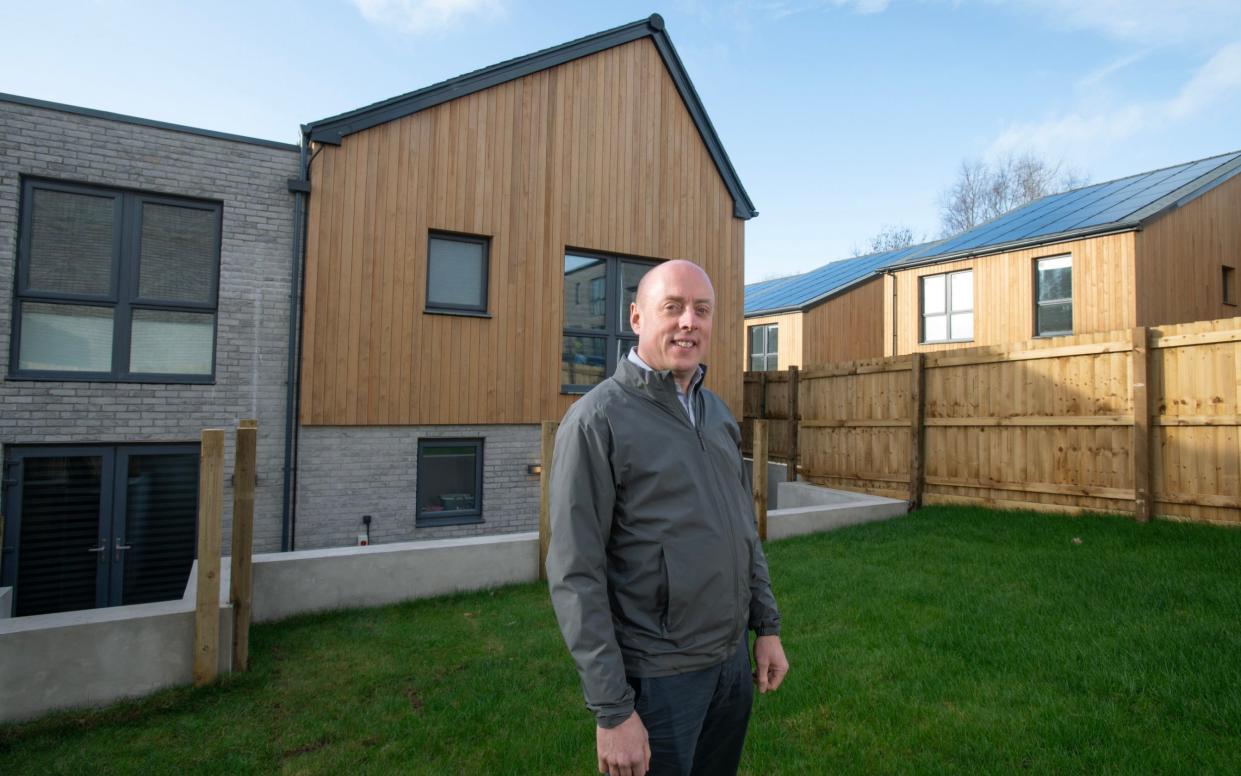
But for Mark Puddicombe, a building surveyor who lives in Pinhoe, Exeter, it makes no difference – because his annual energy bill is fixed at precisely £0.
How Mr Puddicombe, 49, can do this is fairly simple – his provider, Octopus Energy, offers him a unique tariff which means he does not pay for his energy all year, making his three-bedroom property a “zero bills home”.
Why Mr Puddicombe is allowed to use energy for free is a bit more complicated.
What is a zero bills home?
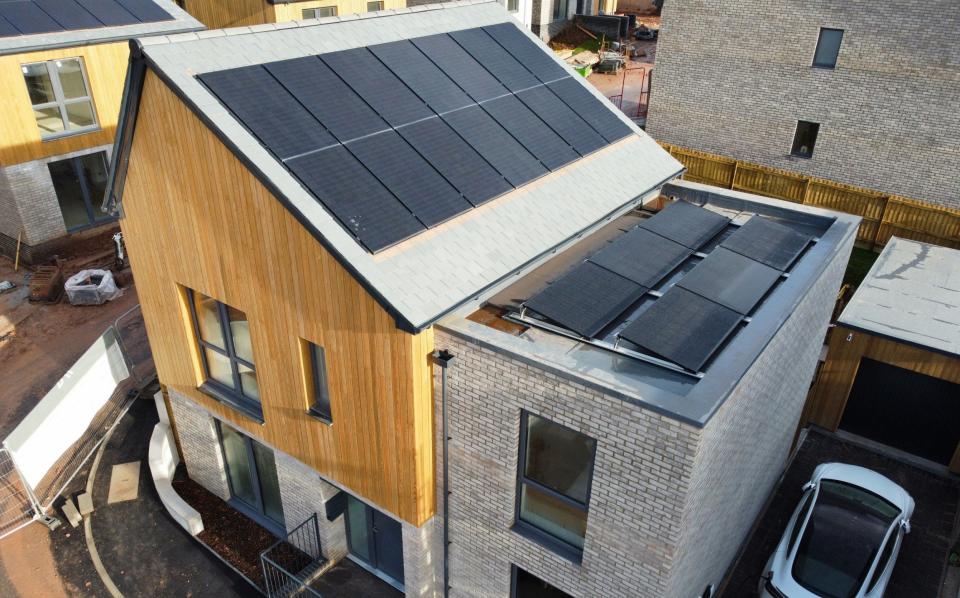
Using an array of 20 solar panels, Mr Puddicombe’s house produces more electricity than it uses throughout the year.
The property has a heat pump, because it is not connected to the gas grid. This means Mr Puddicombe uses more electricity than the average home reliant on gas.
But thanks to the power generated by the solar panels, which is stored in a battery, for the most part Mr Puddicombe’s home meets its own energy needs without relying on the electricity grid.
Without the tariff from his supplier, Mr Puddicombe’s annual energy bill would be in the region of a few hundred pounds a year.

This is because in the winter months, when Mr Puddicombe’s energy use is at its highest, he is a “net importer” of electricity, and must rely on the grid, as the panels and batteries cannot generate and store enough power to keep the home running.
But in the summer months, when solar panels are most effective, the property generates more energy than it needs. The surplus is sold back to the grid at times of high demand, making Mr Puddicombe a “net exporter”.
Mr Puddicombe’s supplier handles the process automatically and sells the electricity to the grid at the best possible rate for maximum profit, which makes up for the periods when homes like Mr Puddicombe’s are using power essentially for free.
The Zero Bill Homes project is a joint undertaking between Octopus Energy and a number of housing developers.
Mr Puddicombe’s house is part of a development built by Verto, but a handful of other developers – including The Hill Group and Clarion Housing Group, a social housing provider – have also announced plans to develop zero bills properties.
The effect on house prices
Close to 1,000 homes have been accredited by Octopus so far, but Michael Cottrell, of the supplier, said the tariff could work for “a number of house types” provided they were not connected to the gas grid, were well insulated, and had enough solar panels.
He estimated that 20 panels would be needed to generate enough power, although homes with as few as 18 have achieved the required standard.
“You wouldn’t put this much solar on a roof if you were just trying to meet a household’s needs,” he said. “We need to over-spec it so it delivers more power than the house consumes.”
The scheme is an obvious fit for new builds, which from 2025 will be required by law to install a heat pump rather than a gas boiler as the Government pushes towards its net zero goals.
However, the scheme relies on covering the roof with solar panels and installing a battery. Doing so costs developers an estimated £15,000, but can add as much as £50,000 to the value of the property, Mr Cottrell claimed.

For Mr Puddicombe, who moved into the property this year, not having to worry about shock energy bill increases alongside high mortgage rates has been a relief. The energy bill in his previous home, built in the 1900s, was around £2,400 a year, he says.
He bought his new home for £595,000, taking out a five-year fixed rate mortgage, with an interest rate of 4.06pc which costs around £2,000 a month in repayments.
Could your home be ‘zero bills’?
Though the focus is on new builds, which are designed with energy efficiency in mind, retrofitting properties to meet the standards of the scheme is still possible, Mr Cottrell said.
“We think anything built from 2015 onwards, under building regulations set out in 2013, is probably well insulated enough,” he said.
“The only constraining factor becomes the roof size – can you get enough solar panels on the roof?”
Most homes with solar panels have between four and five, and a big installation would have nine to 12. Typically homeowners install panels only on the sun-facing side of the roof, while zero-bills homes require the entire surface to be covered.
Mr Cottrell admits that a roof would have to be designed with solar in mind to accommodate that many panels, and so would need to be pitched.
Using green technology to reduce bills is still within the reach of homeowners able to pay for upgrades, however.
Early adopters of solar technology, batteries and EVs have made use of export tariffs to pay off their investments quickly. But it is worth noting that schemes that allowed homeowners to sell power to the grid were more generous in the past.
Regardless, with energy bills unlikely to fall to the levels they were before the Ukraine war, the premium on properties with energy-saving technology already installed has risen.
Last year, a Rightmove study found a correlation between higher Energy Performance Certificate ratings and higher house prices. EPC B-rated houses are now the most in demand from buyers.
Homeowners are also expected to face a “boiler tax” on replacing gas heating systems, as boiler manufacturers raise prices by as much as £120 to offset fines the Government will enforce on manufacturers for missing heat pump sales targets.
Recommended
What is ‘net zero’, and how much will it cost you?
Have you dramatically cut your energy bills? We want to hear from you, email tom.haynes@telegraph.co.uk

