Putnam Update: Coronavirus Outbreak FAQ
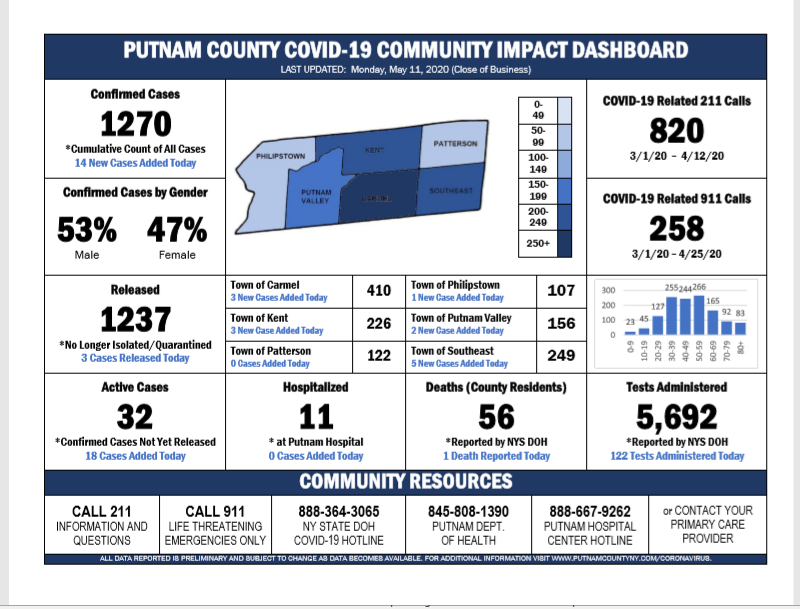
PUTNAM COUNTY, NY — The new coronavirus pandemic in Putnam County continues, with a total as of Monday of 1,270 people having tested positive since the outbreak began, out of a total of 5,692 people tested, according to the Health Department.
There are 32 active cases in the county, with 18 cases added Monday and just 3 released, health officials said. Eleven people with COVID-19 are at Putnam County Hospital Center. With one death reported yesterday, the death toll stood at 56.
Officials at the Putnam County Department of Health report fielding many questions regarding testing. They offered these answers to some of the most frequently asked questions.
What are the different testing options?
There are three types of COVID-19 tests: diagnostic (or PCR), antibody (or serum) and antigen. Diagnostic tests were the first COVID-19 tests available and identifies active infections. As of May 10, the FDA has given emergency use authorization, or EUA, to several antibody tests and one antigen test. Many more tests are on the market, but have not received an EUA. The FDA permits this under a special emergency policy, as long as the test is validated by the manufacturer and test results do not claim the ability to diagnose COVID-19 or prove immunity. At this time, the FDA does not allow any serological (blood) tests to be performed at home, so all tests must be conducted in clinical labs or by health care workers.
Why is there so much focus on antibody testing now?
COVID-19 antibody testing is taking place across the state by NYSDOH and healthcare providers. Antibody testing identifies if a person has ever been exposed to the novel coronavirus. A positive antibody result means that a person may currently be ill, had the virus and recovered, or that they were exposed to the virus and did not develop symptoms. Scientists and doctors do not yet know if a positive antibody test indicates if a person has immunity against the virus or how long that immunity might last.
Antibody testing helps public health professionals begin to determine the prevalence or how common the virus is in the population. It also allows for the identification of people who are eligible to donate plasma to be used in trials as a potential treatment for COVID-19. For more information about plasma donations, please visit https://www.nybc.org/
The New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH) is conducting a prevalence study through random antibody testing across NYS. They will never ask for payment, insurance information or your social security number to perform this testing. If you receive a letter, email or phone call asking for these things, DO NOT give out this information.
What is an antibody test?
COVID-19 antibody tests are used by healthcare providers to identify people who have previously been exposed to the virus. These tests are NOT reliable enough to draw any conclusions regarding protection from future coronavirus infections.
How is it collected?
These are blood collection tests, usually taken from a finger. Some results are available within a few minutes while others may take a few days.
What is actually being tested?
These blood tests look for antibodies to COVID-19. Antibodies are produced in response to an infectious agent. COVID-19 antibodies generally arise after four to ten days after infection.
Is it accurate?
Without undergoing the complete FDA approval process, there are likely to be quality control concerns. All tests that have been given EUA should bear a label stating, “This test has not been reviewed by the FDA.” This label will be visible to the laboratory but not always to the consumer. Every antibody test on the market is different. Speak to your physician about the antibody test they offer.
Bottom line: Current COVID-19 antibody test results should not be used to make individual decisions about returning to work or changes to social distancing. For example, if a test indicates you do have antibodies, you may still be able to get sick again from the virus , so hand hygiene and social and physical distancing are still important. This information is subject to change based on scientific research. The practical value of these tests is to provide public health experts with good information about rates of infection and disease spread throughout a community.
What is the diagnostic test?
Diagnostic tests, or PCR tests, are used by healthcare providers to identify people who are currently infected with COVID-19.
How is it collected?
Typically mucus from a person’s throat and/or nose is collected. (Saliva testing is still being studied.) Results from this diagnostic test can be provided within minutes (rapid testing) or may take a few days.
What is actually being tested?
PCR tests look for the genetic material of this novel coronavirus. PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology amplifies any detectable viral genetic material, only present when a person is actively infected.
Is it accurate?
Currently, these are the most reliable tests. However, because it may take a few days before the virus sheds in the throat and nose, the timing of testing can impact results. In other words, this test may not identify an infection from a recent exposure.
Bottom line: While this is the most reliable form of diagnostic test for COVID-19, some studies show certain rapid diagnostic tests may miss nearly 10% of cases.
What is the antigen test?
This test may be used as a quick point-of-care test to detect active infections. It is not used to diagnose disease, but may be used to screen people and identify those that should have further diagnostic testing.
How is it collected?
This test is performed by a swab and culture of the nasal cavity with results potentially available within minutes.
What is actually being tested?
Antigen tests look for proteins on the surface of the virus. This is quite different from diagnostic tests that identify genetic material inside of the virus.
Is it accurate?
Researchers say that antigen testing reliability runs the gamut. One of the main advantages of an antigen test is the speed of the test, which can provide results in minutes. However, antigen tests may not detect all active infections, as they do not work the same way as a PCR test. This means that positive results from antigen tests are highly accurate, but there is a higher chance of false negatives, so negative results do not rule out infection and likely will need to be confirmed with a PCR test. More information on COVID-19 antigen test accuracy will become available as these tests reach the market. As of May 10, there has been one antigen test authorized by the FDA through EUA.
Bottom Line: Because these tests are quick, when they are found to be reliable, they might be used as a primary screening tool for people in hospitals, certain workplaces, or in other situations in which the person has the potential to spread disease to large numbers of people, or particularly vulnerable people. Quality control procedures will need to ensure results are reliable and that follow-up testing is conducted to diagnose active cases or make full medical diagnoses.
What is meant if a test is highly sensitive or highly specific?
Sensitivity and specificity are the two measures that describe how reliable a test is. Sensitivity measures the percentage of people, on average that the test correctly identifies as having antibodies. Specificity measures the percentage of people, on average that the test correctly identifies as not having antibodies.
A highly sensitive test will have a low false negative rate, meaning the test will correctly identify positive cases at a high rate. A test with high specificity will have a low false positive rate, meaning the test will correctly identify negatives cases at a high rate. The best tests have high sensitivity and high specificity.
Where can I get tested?
There are dozens of antibody and diagnostic testing locations throughout the county and the state. Call your healthcare provider to find out if they offer testing. The NYSDOH continues to run diagnostic testing sites. To find out if you meet the guidelines for testing, you can take an online assessment at https://covid19screening.health.ny.gov/.
For additional testing questions or information, email COVID19@putnamcountyny.gov
This article originally appeared on the Southeast-Brewster Patch

