Where do most hurricanes hit in Texas? See storm strikes by county since 1900
The 2024 Atlantic hurricane season doesn't begin until June 1 but forecasters are already warning the season could be a very active one.
The reason? The combination of La Niña and record-warm water temperatures. La Niña, unlike its counterpart El Niño, actually helps tropical cyclones develop by reducing wind shear in the Atlantic basin. Water warm helps fuel tropical storms and hurricanes.
Active La Niña years in 2005 and 2020 set records for the number of named storms.
Here's a look at when and where named storms have historically formed in the Atlantic basin, which covers the northern Atlantic Ocean, Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico.
When is the Atlantic hurricane season?
The Atlantic hurricane season runs from June 1 through Nov. 30, although storms have formed as early as January and as late as December.
The National Hurricane Center starts issuing its daily tropical outlook reports on May 15. If a storm forms before then, a special report is issued for the life of that storm.
Hurricane tracker: Tropical Storm Harold makes landfall in Texas in 2023. Follow its path.
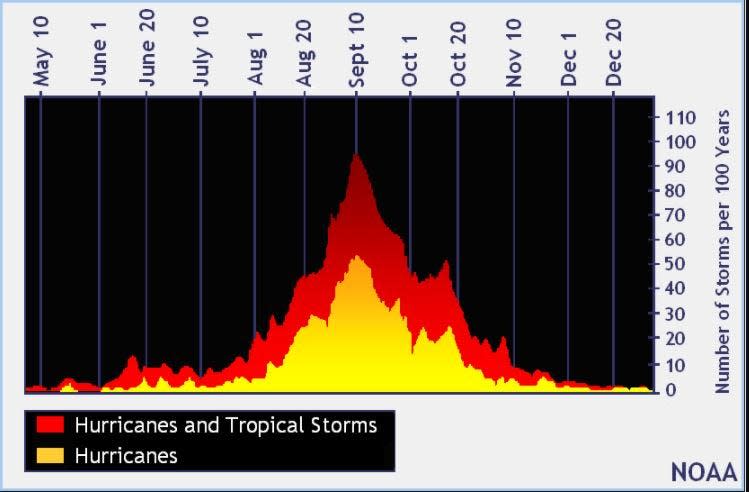
When is the peak of the Atlantic hurricane season?
The Atlantic hurricane season is most active between August and October, with the peak occurring Sept. 10.
How do hurricanes form?
Warm water "can provide more fuel for storms, potentially leading to a higher number of storms and possibly greater intensity," said Hui Li, a project scientist at the University Corporate for Atmospheric Research.
Seasonal forecasters are very closely monitoring the Eastern Atlantic, where sea surface temperatures in the region off the African coast are 1, 2 and even 3 degrees Celsius warmer than normal right now, Jason Dunion, a meteorologist at the University of Miami, said. "And it's not even spring yet."
How do hurricanes form? An inside look at the birth and power of ferocious storms
More than half the tropical systems each year come from that "hurricane nursery," and 80% to 85% of the major hurricanes, Dunion said. So it's "a really important place."
With warm temperatures to the east and less wind shear to the west, Dunion said, storms could get a boost from both sides as they advance across the Atlantic Ocean.
At what point do storms change from tropical depressions up to major hurricanes?
Here's an explanation of each of the common terms used by the National Hurricane Center. A tropical cyclone is the generic term for everything from tropical depressions to hurricanes:
Tropical depression: A tropical cyclone with maximum sustained winds of 38 mph (33 knots) or less.
Tropical storm: A tropical cyclone with maximum sustained winds of 39 to 73 mph (34 to 63 knots).
Hurricane: A tropical cyclone with maximum sustained winds of 74 mph (64 knots) or higher. In the western North Pacific, hurricanes are called typhoons; similar storms in the Indian Ocean and South Pacific Ocean are called cyclones.
Major hurricane: A tropical cyclone with maximum sustained winds of 111 mph (96 knots) or higher, corresponding to a Category 3, 4 or 5 on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale.
What does La Niña mean for the 2024 hurricane season?
La Niña, a pattern of cooler waters along the equator in the Pacific Ocean, often leads to more active hurricane seasons. It tends to reduce vertical wind shear over the Atlantic and allow budding tropical storms to build high cloud structures that can supercharge their energy.
Meanwhile, sea surface temperatures in the tropical Atlantic are already running above normal, even warmer than last year. Ocean surface temperatures globally set another new record high, reaching 21.13 degrees Celsius last Wednesday, or just over 70 degrees Fahrenheit, according to the most recent data available through the University of Maine's Climate Reanalyzer. That's a slight increase above the 21.1 degree-record set last April and again last August.
Hurricane season forecast is already looking grim: Here's why hot oceans, La Niña matter
Where have hurricanes hit in Texas?
Among Texas cities, Houston, Galveston and others along the Gulf Coast experience the most hurricanes.
Click here for a complete list of hurricanes that have affected North Texas since 1877.
Total number of hurricane strikes by county
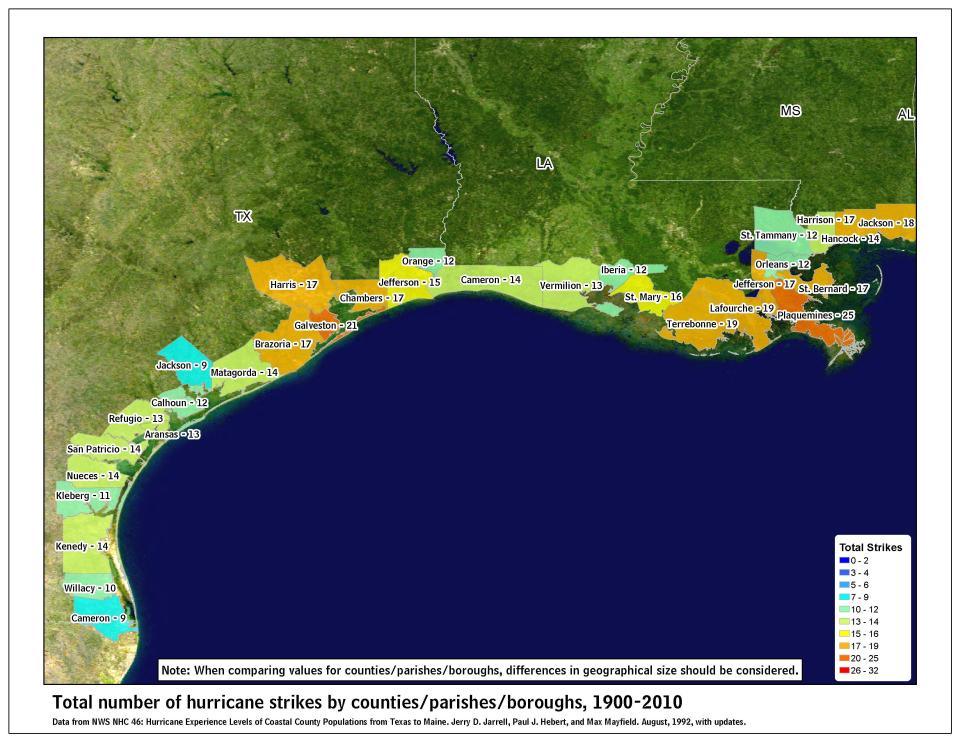
Maps show the number of hurricanes that occurred in each county along the U.S. coastline from 1900 to 2010.
How many major hurricanes have hit your county?
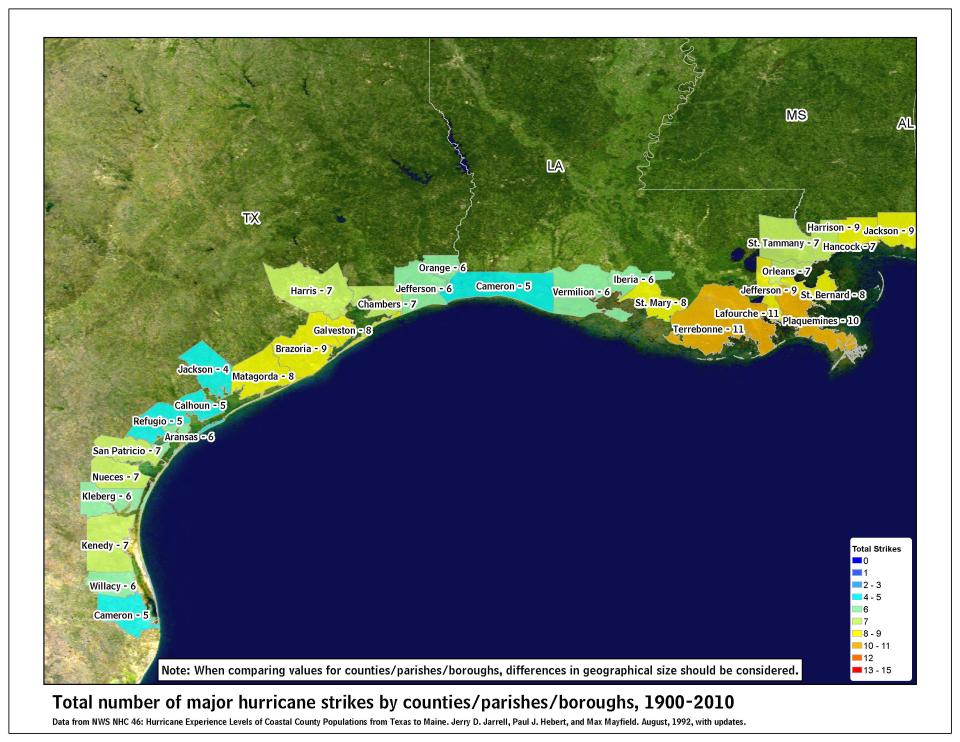
Maps show how many major hurricanes have hit each county along the U.S. coastline from 1900 to 2010.
A major hurricane is one that is Category 3 or higher, with maximum sustained winds of at least 111 mph.
List of top 10 deadliest hurricanes in Texas
Here are the top 10 deadliest hurricanes to hit Texas from 1851 to 2010, according to data gathered by NOAA:
Galveston Hurricane of 1900 (Category 4): Death toll between 8,000 and 12,000, named the deadliest hurricane in U.S. history
Hurricane Audrey (1957, Category 4): 416
Galveston Hurricane of 1915 (Category 4): 275
Unnamed (1875, Category 3): 176
Indianola Hurricane (1886, Category 4): 150
Hurricane Carla (1961, Category 4): 46, named the largest hurricane of record in Texas
Velasco Hurricane (1909, Category 3): 41
Freeport Hurricane (1932, Category 4): 40
Cuba–Brownsville Hurricane (1933, Category 3): 40
Louisiana–Texas Hurricane (1918, Category 3): 34
List of top 5 costliest hurricanes in Texas
Here are the top 5 costliest hurricanes to hit Texas since 1851to 2010, according to data gathered by NOAA:
Hurricane Ike (2008, Category 2): $29.52 billion
Hurricane Rita (2005, Category 3): $12.04 billion
Hurricane Alicia (1983, Category 3): $3 billion
Hurricane Dolly (2008, Category 1): $1.05 billion
Hurricane Celia (1970, Category 3): $930 million
Track the latest hurricanes in the Atlantic Ocean
This article originally appeared on Austin American-Statesman: La Niña, warm temps could mean a very active 2024 hurricane season

