Should We Worry About Viking Line ABP’s (HEL:VIK1V) P/E Ratio?

Want to participate in a short research study? Help shape the future of investing tools and you could win a $250 gift card!
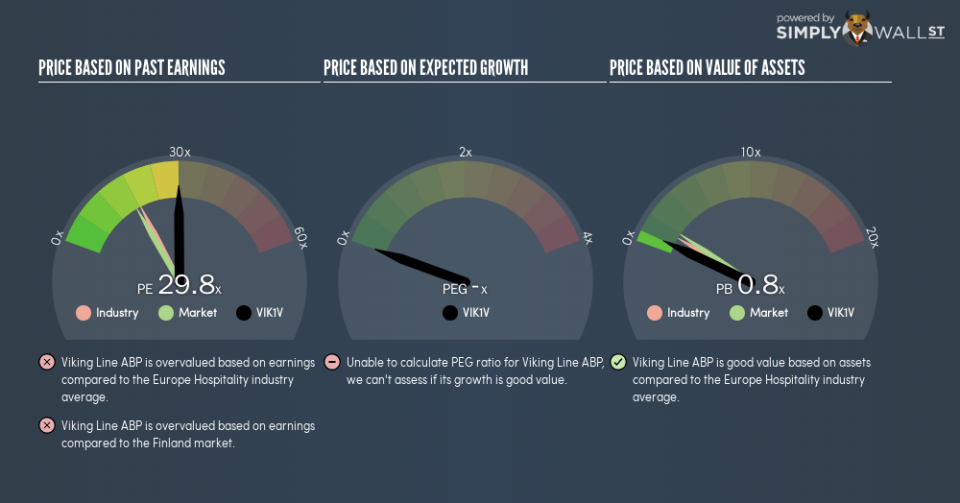
The goal of this article is to teach you how to use price to earnings ratios (P/E ratios). We’ll show how you can use Viking Line ABP’s (HEL:VIK1V) P/E ratio to inform your assessment of the investment opportunity. Viking Line ABP has a price to earnings ratio of 29.8, based on the last twelve months. That means that at current prices, buyers pay €29.8 for every €1 in trailing yearly profits.
View our latest analysis for Viking Line ABP
How Do You Calculate A P/E Ratio?
The formula for price to earnings is:
Price to Earnings Ratio = Share Price ÷ Earnings per Share (EPS)
Or for Viking Line ABP:
P/E of 29.8 = €15.2 ÷ €0.51 (Based on the year to December 2018.)
Is A High P/E Ratio Good?
A higher P/E ratio means that investors are paying a higher price for each €1 of company earnings. All else being equal, it’s better to pay a low price — but as Warren Buffett said, ‘It’s far better to buy a wonderful company at a fair price than a fair company at a wonderful price.’
How Growth Rates Impact P/E Ratios
If earnings fall then in the future the ‘E’ will be lower. Therefore, even if you pay a low multiple of earnings now, that multiple will become higher in the future. A higher P/E should indicate the stock is expensive relative to others — and that may encourage shareholders to sell.
Viking Line ABP increased earnings per share by 3.9% last year. In contrast, EPS has decreased by 35%, annually, over 5 years.
How Does Viking Line ABP’s P/E Ratio Compare To Its Peers?
We can get an indication of market expectations by looking at the P/E ratio. You can see in the image below that the average P/E (19.2) for companies in the hospitality industry is lower than Viking Line ABP’s P/E.
Viking Line ABP’s P/E tells us that market participants think the company will perform better than its industry peers, going forward. Shareholders are clearly optimistic, but the future is always uncertain. So further research is always essential. I often monitor director buying and selling.
A Limitation: P/E Ratios Ignore Debt and Cash In The Bank
The ‘Price’ in P/E reflects the market capitalization of the company. That means it doesn’t take debt or cash into account. Hypothetically, a company could reduce its future P/E ratio by spending its cash (or taking on debt) to achieve higher earnings.
Such expenditure might be good or bad, in the long term, but the point here is that the balance sheet is not reflected by this ratio.
Is Debt Impacting Viking Line ABP’s P/E?
Viking Line ABP has net debt worth 40% of its market capitalization. This is a reasonably significant level of debt — all else being equal you’d expect a much lower P/E than if it had net cash.
The Verdict On Viking Line ABP’s P/E Ratio
Viking Line ABP’s P/E is 29.8 which is above average (17.2) in the FI market. With modest debt relative to its size, and modest earnings growth, the market is likely expecting sustained long-term growth, if not a near-term improvement.
When the market is wrong about a stock, it gives savvy investors an opportunity. As value investor Benjamin Graham famously said, ‘In the short run, the market is a voting machine but in the long run, it is a weighing machine.’ We don’t have analyst forecasts, but you could get a better understanding of its growth by checking out this more detailed historical graph of earnings, revenue and cash flow.
But note: Viking Line ABP may not be the best stock to buy. So take a peek at this free list of interesting companies with strong recent earnings growth (and a P/E ratio below 20).
To help readers see past the short term volatility of the financial market, we aim to bring you a long-term focused research analysis purely driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis does not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements.
The author is an independent contributor and at the time of publication had no position in the stocks mentioned. For errors that warrant correction please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com.